Warthin's tumor pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
Nazia Fuad (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Warthin's tumor}} | {{Warthin's tumor}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Ammu}} {{N.F}} | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Warthin's tumor arises from [[salivary gland]] epithelium, which are secretory cells of the [[salivary gland]]. On gross pathology, cystic and multicentric appearance are characteristic findings of Warthin's tumor. On microscopic histopathological analysis, papillae, fibrous [[capsule]], and cystic spaces are characteristic findings of Warthin's tumor. | |||
==Pathogenesis== | == Pathophysiology == | ||
===Pathogenesis=== | |||
* | The exact pathogenesis of warthins tumor is not completely understood. Acording to a study in 2016,<ref name="KuzenkoRomanuk20162">{{cite journal|last1=Kuzenko|first1=Yevhen V.|last2=Romanuk|first2=Anatoly M.|last3=Dyachenko|first3=Olena Olegivna|last4=Hudymenko|first4=Olena|title=Pathogenesis of Warthin’s tumors|journal=Interventional Medicine and Applied Science|volume=8|issue=2|year=2016|pages=41–48|issn=2061-1617|doi=10.1556/1646.8.2016.2.2}}</ref> : | ||
* The | *[[Stroma]] and [[parenchyma]] of the [[tumor]] was histopathologically analyzed. | ||
* | *The [[epithelial]] and [[stromal]] component was equally distributed in [[tumor]] mass. | ||
*This study showed that the Warthin's tumor occurs as a result of of [[inflammatory]] process. | |||
*[[Epithelial]] part of the Warthin's tumor is the main trigger for the [[tumor]] process. | |||
==Genetics== | ==Genetics== | ||
*Expression of CRTC1 - MAML2 chimeric genes through t(11;19)(q21;p13) translocation is involved in the pathogenesis of Warthin's tumor. | |||
==Gross Pathology== | |||
Characteristic findings of warthin's tumor on gross pathology are; | |||
* Size of the [[tumor]] varies between 2-5 cm. | |||
* The [[tumor]] is well demarcated, grey yellow in color. | |||
* It is encapsulated, [[Lobular|lobulated]] and multicentric. | |||
* Warthin;s tumor can be fixed to overlying skin. | |||
* 10-15% are multifocal/bilateral. | |||
* Tumor can have serous/mucinous secretion. | |||
== | ==Microscopic Pathology== | ||
On microscopic histopathological analysis the characteristic findings of warthin;s tumor are; | |||
* Dense lymphoid stroma with double layer of epithelial cells resting on the stroma. | |||
* The cystic spaces are present which are narrowed by polypoid projections. | |||
* Basal cell layer is not continuous and is interrupted in places . | |||
* The oncocytic columnar cells palisade on the surface. | |||
* There is no myoepithelial component present in tumor. | |||
* Occasional features include [[Cilia|cilia,]] [[squamous metaplasia]] with [[Necrosis|necrosis,]] [[Mast cell|mast cells]], [[dendritic cells]] and [[Sebaceous|sebaceous cells]]. | |||
= | [[image:Warthin tumor (1).jpg|center|400px|thumb| CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=507400]] | ||
[[image:Warthin tumor (2).jpg|center|400px|thumb| CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=507402]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | {{WikiDoc Sources}} | ||
[[Category:Oral pathology]] | [[Category:Oral pathology]] | ||
| Line 49: | Line 46: | ||
[[Category:Mature chapter]] | [[Category:Mature chapter]] | ||
[[Category:Disease]] | [[Category:Disease]] | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Oncology]] | |||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Otolaryngology]] | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:53, 21 January 2019
|
Warthin's tumor Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Warthin's tumor pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Warthin's tumor pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Warthin's tumor pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ammu Susheela, M.D. [2] Nazia Fuad M.D.
Overview
Warthin's tumor arises from salivary gland epithelium, which are secretory cells of the salivary gland. On gross pathology, cystic and multicentric appearance are characteristic findings of Warthin's tumor. On microscopic histopathological analysis, papillae, fibrous capsule, and cystic spaces are characteristic findings of Warthin's tumor.
Pathophysiology
Pathogenesis
The exact pathogenesis of warthins tumor is not completely understood. Acording to a study in 2016,[1] :
- Stroma and parenchyma of the tumor was histopathologically analyzed.
- The epithelial and stromal component was equally distributed in tumor mass.
- This study showed that the Warthin's tumor occurs as a result of of inflammatory process.
- Epithelial part of the Warthin's tumor is the main trigger for the tumor process.
Genetics
- Expression of CRTC1 - MAML2 chimeric genes through t(11;19)(q21;p13) translocation is involved in the pathogenesis of Warthin's tumor.
Gross Pathology
Characteristic findings of warthin's tumor on gross pathology are;
- Size of the tumor varies between 2-5 cm.
- The tumor is well demarcated, grey yellow in color.
- It is encapsulated, lobulated and multicentric.
- Warthin;s tumor can be fixed to overlying skin.
- 10-15% are multifocal/bilateral.
- Tumor can have serous/mucinous secretion.
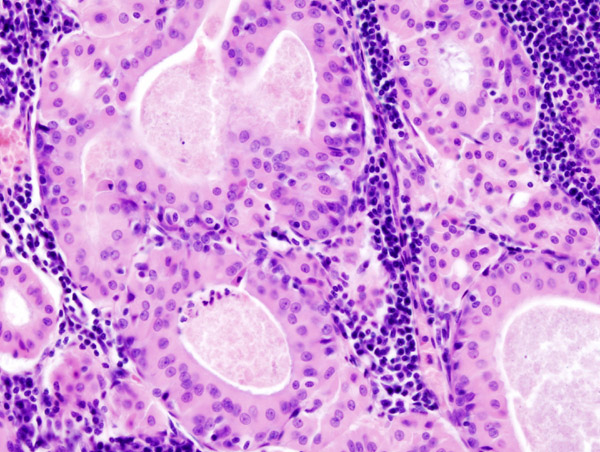
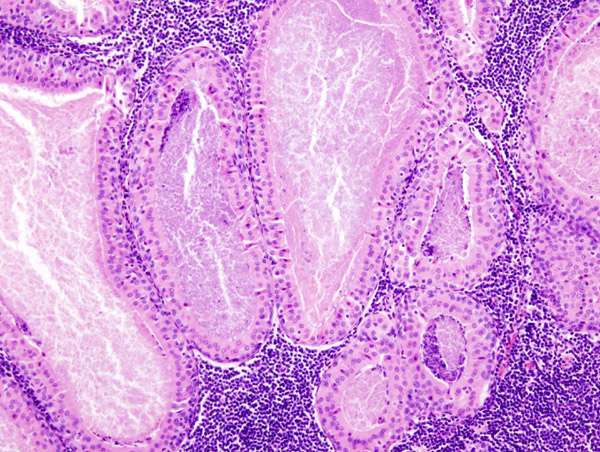
Microscopic Pathology
On microscopic histopathological analysis the characteristic findings of warthin;s tumor are;
- Dense lymphoid stroma with double layer of epithelial cells resting on the stroma.
- The cystic spaces are present which are narrowed by polypoid projections.
- Basal cell layer is not continuous and is interrupted in places .
- The oncocytic columnar cells palisade on the surface.
- There is no myoepithelial component present in tumor.
- Occasional features include cilia, squamous metaplasia with necrosis, mast cells, dendritic cells and sebaceous cells.
References
- ↑ Kuzenko, Yevhen V.; Romanuk, Anatoly M.; Dyachenko, Olena Olegivna; Hudymenko, Olena (2016). "Pathogenesis of Warthin's tumors". Interventional Medicine and Applied Science. 8 (2): 41–48. doi:10.1556/1646.8.2016.2.2. ISSN 2061-1617.