Uveal melanoma other imaging findings: Difference between revisions
Simrat Sarai (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Uveal melanoma}} | {{Uveal melanoma}} | ||
{{CMG}}{{AE}}{{Simrat}} | {{CMG}}{{AE}}{{Simrat}} {{Fs}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
[[PET scan]], [[ultrasound]] biomicroscopy, [[optical coherence tomography]], color [[fundus]] photography, [[fluorescein angiography]], indocyanine green [[angiography]], [[transillumination]], and photography may be helpful in the [[diagnosis]] of uveal melanoma. | |||
==Other Imaging Findings== | ==Other Imaging Findings== | ||
=== | [[PET scan]], [[ultrasound]] biomicroscopy, [[optical coherence tomography]], color [[fundus]] photography, [[fluorescein angiography]], indocyanine green [[angiography]], [[transillumination]], and photography may be helpful in the [[diagnosis]] of uveal melanoma.<ref name="NCI">Uveal melanoma. National Cancer Institute(2015) http://www.cancer.gov/types/eye/patient/intraocular-melanoma-treatment-pdq Accessed on October 24 2015</ref> | ||
===Positron Emission Tomography Scan=== | |||
* A baseline [[PET scan]] of the [[liver]] and other [[Abdomen|abdominal]] [[Organ (anatomy)|organs]] is recommended in pati[[e]]<nowiki/>nts with a uveal melanoma. [[Tumors]] that are too small will be identified by this study.<ref name="Finger2005">{{cite journal|last1=Finger|first1=P T|title=Whole body PET/CT for initial staging of choroidal melanoma|journal=British Journal of Ophthalmology|volume=89|issue=10|year=2005|pages=1270–1274|issn=0007-1161|doi=10.1136/bjo.2005.069823}}</ref> | |||
<ref name="Reddy2005">{{cite journal|last1=Reddy|first1=S|title=PET/CT imaging: detection of choroidal melanoma|journal=British Journal of Ophthalmology|volume=89|issue=10|year=2005|pages=1265–1269|issn=0007-1161|doi=10.1136/bjo.2005.066399}}</ref> | |||
[[File:Choroidal melanoma on FDG PET CT.jpg|thumb|none|200px|choroidal melanoma on FDG PET CT<ref name="radio1">Image courtesy of Dr. Preveen Jha [http://www.radiopaedia.org Radiopaedia] (original file [http://radiopaedia.org/cases/choroidal-melanoma-1]).[http://radiopaedia.org/licence Creative Commons BY-SA-NC</ref>]] | |||
<br /> | |||
===Optical coherence tomography=== | ===Optical coherence tomography=== | ||
Optical coherence tomography is a test that uses light waves instead of sound waves to create very detailed images of the back of the eye (fundus). | |||
*[[Optical coherence tomography]] is a [[Test-retest|test]] that uses light waves instead of [[sound]] waves to create very detailed [[images]] of the back of the [[eye]] ([[fundus]]).<ref name="Antcliffffytche2000">{{cite journal|last1=Antcliff|first1=Richard J|last2=ffytche|first2=Timothy J|last3=Shilling|first3=John S|last4=Marshall|first4=John|title=Optical coherence tomography of melanocytoma|journal=American Journal of Ophthalmology|volume=130|issue=6|year=2000|pages=845–847|issn=00029394|doi=10.1016/S0002-9394(00)00629-2}}</ref> | |||
===Color fundus photography=== | ===Color fundus photography=== | ||
* Color fundus photography photographs of the [[Fundus (eye)|fundus]] helps to show whether the [[tumor]] looks the same as before treatment or not. | |||
===Fluorescein angiography=== | ===Fluorescein angiography=== | ||
Fluorescein angiography | |||
* [[Fluorescein angiography]] is a procedure to look at [[blood vessels]] inside the [[eye]].<ref name="PettitBarton1970">{{cite journal|last1=Pettit|first1=T. H.|last2=Barton|first2=A.|last3=Foos|first3=R. Y.|last4=Christensen|first4=R. E.|title=Fluorescein Angiography of Choroidal Melanomas|journal=Archives of Ophthalmology|volume=83|issue=1|year=1970|pages=27–38|issn=0003-9950|doi=10.1001/archopht.1970.00990030029006}}</ref> | |||
===Indocyanine green angiography=== | ===Indocyanine green angiography=== | ||
Indocyanine green angiography is a procedure to look at blood vessels in the choroid layer of the eye. | |||
* Indocyanine green [[angiography]] is a procedure to look at [[blood vessels]] in the [[choroid]] layer of the [[eye]]. <ref name="Mueller1998">{{cite journal|last1=Mueller|first1=Arthur J.|title=Imaging the Microvasculature of Choroidal Melanomas With Confocal Indocyanine Green Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy|journal=Archives of Ophthalmology|volume=116|issue=1|year=1998|pages=31|issn=0003-9950|doi=10.1001/archopht.116.1.31}}</ref> | |||
===Transillumination=== | ===Transillumination=== | ||
Transillumination is an exam of the iris, cornea, lens, and ciliary body with a light placed on either the upper or lower lid. | |||
===Photography=== | * Transillumination is an exam of the [[iris]], [[cornea]], [[lens]], and [[ciliary body]] with a light placed on either the upper or lower lid. <ref name="Umlas1997">{{cite journal|last1=Umlas|first1=James|title=Comparison of Transillumination and Histologic Slide Measurements of Choroidal Melanoma|journal=Archives of Ophthalmology|volume=115|issue=4|year=1997|pages=474|issn=0003-9950|doi=10.1001/archopht.1997.01100150476004}}</ref> | ||
High resolution digital cameras are used to take pictures of the inside and outside of the eye and to view the structures in the back and front of the eye. These photographs are important for documenting the tumor and its relationship to important structures of the eye. By comparing photographs before and after treatment, they can help determine whether the treatment given is effective. | |||
*We may see the [[tumor]] as a dark shadow with well-defined margins. | |||
===Photography=== | |||
* High resolution digital cameras are used to take pictures of the inside and outside of the [[eye]] and to view the structures in the back and front of the [[eye]]. | |||
* These photographs are important for documenting the [[tumor]] and its relationship to important structures of the [[eye]]. | |||
* By comparing photographs before and after treatment, they can help determine whether the treatment given is effective. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
{{ | {{reflist|2}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | |||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
[[Category:Ophthalmology]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Oncology]] | |||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Ophthalmology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:56, 13 August 2019
|
Uveal melanoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Uveal melanoma other imaging findings On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Uveal melanoma other imaging findings |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Uveal melanoma other imaging findings |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [2]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Simrat Sarai, M.D. [3] Fahimeh Shojaei, M.D.
Overview
PET scan, ultrasound biomicroscopy, optical coherence tomography, color fundus photography, fluorescein angiography, indocyanine green angiography, transillumination, and photography may be helpful in the diagnosis of uveal melanoma.
Other Imaging Findings
PET scan, ultrasound biomicroscopy, optical coherence tomography, color fundus photography, fluorescein angiography, indocyanine green angiography, transillumination, and photography may be helpful in the diagnosis of uveal melanoma.[1]
Positron Emission Tomography Scan
- A baseline PET scan of the liver and other abdominal organs is recommended in patients with a uveal melanoma. Tumors that are too small will be identified by this study.[2]
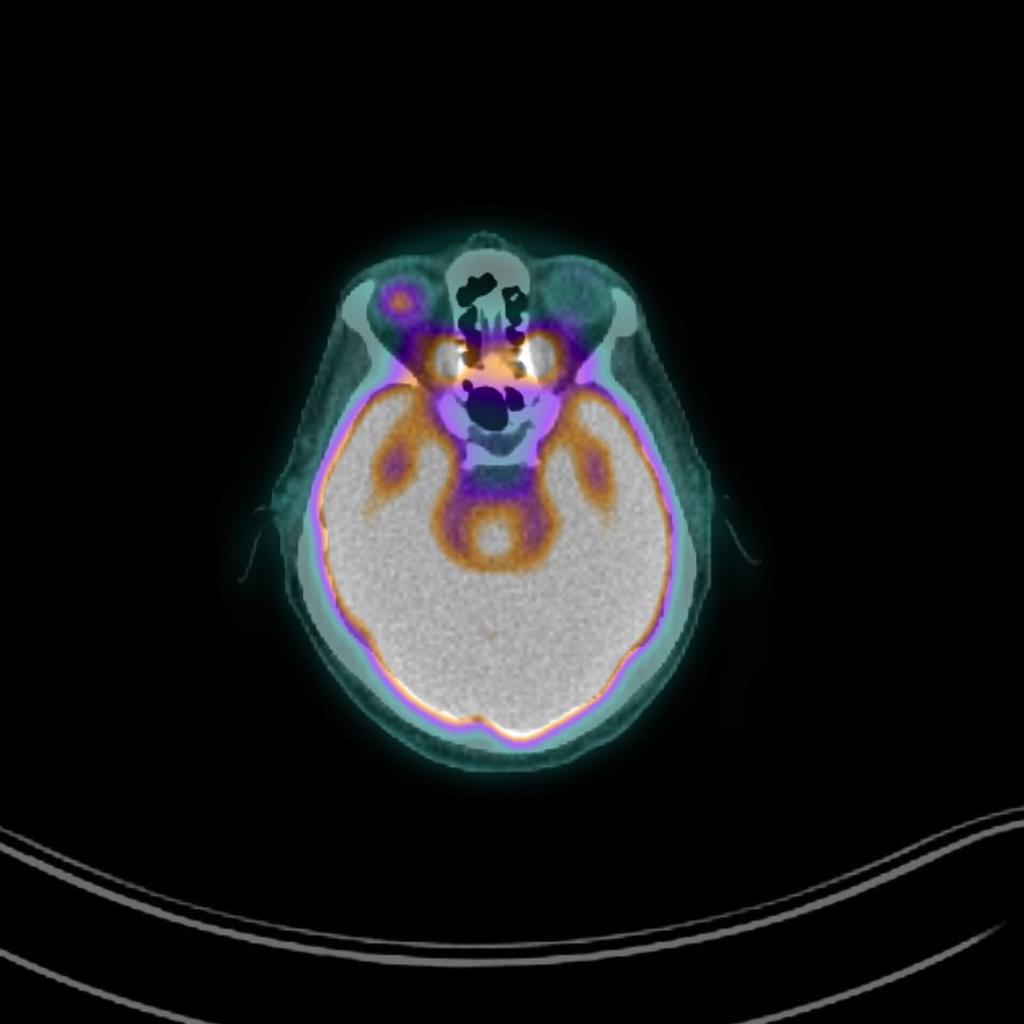
Optical coherence tomography
- Optical coherence tomography is a test that uses light waves instead of sound waves to create very detailed images of the back of the eye (fundus).[5]
Color fundus photography
- Color fundus photography photographs of the fundus helps to show whether the tumor looks the same as before treatment or not.
Fluorescein angiography
- Fluorescein angiography is a procedure to look at blood vessels inside the eye.[6]
Indocyanine green angiography
- Indocyanine green angiography is a procedure to look at blood vessels in the choroid layer of the eye. [7]
Transillumination
- Transillumination is an exam of the iris, cornea, lens, and ciliary body with a light placed on either the upper or lower lid. [8]
- We may see the tumor as a dark shadow with well-defined margins.
Photography
- High resolution digital cameras are used to take pictures of the inside and outside of the eye and to view the structures in the back and front of the eye.
- These photographs are important for documenting the tumor and its relationship to important structures of the eye.
- By comparing photographs before and after treatment, they can help determine whether the treatment given is effective.
References
- ↑ Uveal melanoma. National Cancer Institute(2015) http://www.cancer.gov/types/eye/patient/intraocular-melanoma-treatment-pdq Accessed on October 24 2015
- ↑ Finger, P T (2005). "Whole body PET/CT for initial staging of choroidal melanoma". British Journal of Ophthalmology. 89 (10): 1270–1274. doi:10.1136/bjo.2005.069823. ISSN 0007-1161.
- ↑ Reddy, S (2005). "PET/CT imaging: detection of choroidal melanoma". British Journal of Ophthalmology. 89 (10): 1265–1269. doi:10.1136/bjo.2005.066399. ISSN 0007-1161.
- ↑ Image courtesy of Dr. Preveen Jha Radiopaedia (original file [1]).[http://radiopaedia.org/licence Creative Commons BY-SA-NC
- ↑ Antcliff, Richard J; ffytche, Timothy J; Shilling, John S; Marshall, John (2000). "Optical coherence tomography of melanocytoma". American Journal of Ophthalmology. 130 (6): 845–847. doi:10.1016/S0002-9394(00)00629-2. ISSN 0002-9394.
- ↑ Pettit, T. H.; Barton, A.; Foos, R. Y.; Christensen, R. E. (1970). "Fluorescein Angiography of Choroidal Melanomas". Archives of Ophthalmology. 83 (1): 27–38. doi:10.1001/archopht.1970.00990030029006. ISSN 0003-9950.
- ↑ Mueller, Arthur J. (1998). "Imaging the Microvasculature of Choroidal Melanomas With Confocal Indocyanine Green Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy". Archives of Ophthalmology. 116 (1): 31. doi:10.1001/archopht.116.1.31. ISSN 0003-9950.
- ↑ Umlas, James (1997). "Comparison of Transillumination and Histologic Slide Measurements of Choroidal Melanoma". Archives of Ophthalmology. 115 (4): 474. doi:10.1001/archopht.1997.01100150476004. ISSN 0003-9950.