Spirapril: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{CMG | {{CMG}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
'''Spirapril hydrochloride''' (Renormax) is an [[ACE inhibitor]] [[antihypertensive]] drug used to treat [[hypertension]]. | '''Spirapril hydrochloride''' (Renormax) is an [[ACE inhibitor]] [[antihypertensive]] drug used to treat [[hypertension]]. | ||
It belongs to dicarboxy group of ace inhibitor. | It belongs to dicarboxy group of ace inhibitor. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 41: | ||
[[Category:ACE inhibitors]] | [[Category:ACE inhibitors]] | ||
[[Category:Cardiovascular Drugs]] | [[Category:Cardiovascular Drugs]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Drug]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:51, 23 July 2014
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50% |
| Metabolism | converted to spiraprilat |
| Elimination half-life | 30 to 35 hours |
| Excretion | Hepatic and renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
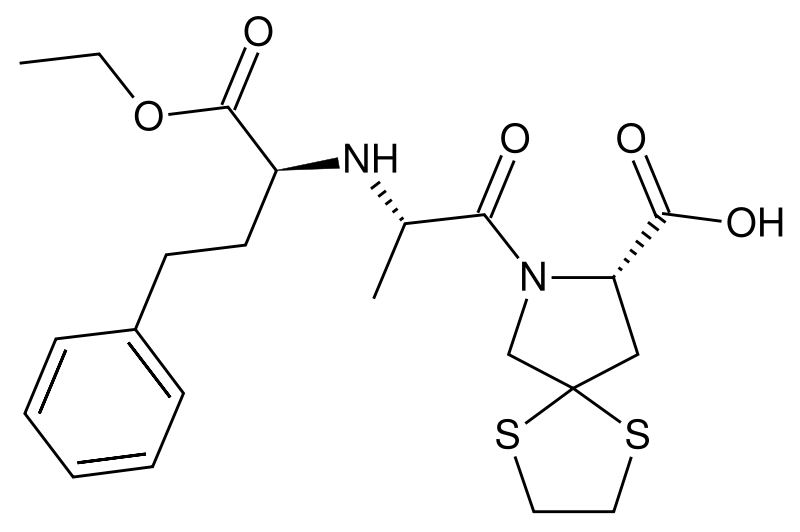
| Formula | C22H30N2O5S2 |
| Molar mass | 466.616 g/mol |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Spirapril hydrochloride (Renormax) is an ACE inhibitor antihypertensive drug used to treat hypertension. It belongs to dicarboxy group of ace inhibitor.
Like many ACE inhibitors, this is a prodrug which is converted to the active metabolite spiraprilat following oral administration. Unlike other members of the group, it is eliminated both by renal and hepatic routes which may allow for greater use in patients with renal impairment.[1] However data on its effect upon the renal function is conflicting.[2]
It is produced synthetically by combining the following two pharmaceutical intermediates:
(S)-1,4-Dithia-7-azaspiro(4,4)-nonane-8-carboxylic acid hydrobromide CAS 75776-79-3
and
N-[1-(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl)-L-Alanine (ECPPA) [2]
Footnotes
- ↑ Shohat J, Wittenberg C, Erman A, Rosenfeld J, Boner G (1999). "Acute and chronic effects of spirapril, alone or in combination with isradipine on kidney function and blood pressure in patients with reduced kidney function and hypertension". Scand J Urol Nephrol. 33 (1): 57&ndash, 62. doi:10.1080/003655999750016294. PMID 10100366.
- ↑ Noble S, Sorkin E (1995). "Spirapril. A preliminary review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of hypertension". Drugs. 49 (5): 750&ndash, 66. doi:10.2165/00003495-199549050-00008. PMID 7601014.
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- ACE inhibitors
- Cardiovascular Drugs
- Drug