Pyridostigmine (patient information): Difference between revisions
m (Protected "Pyridostigmine (patient information)": Robot: Protecting all pages from category Drug ([edit=sysop] (indefinite) [move=sysop] (indefinite))) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage | |||
|authorTag={{AP}} | |||
|genericName=Pyridostigmine | |||
|aOrAn=a | |||
|drugClass=[[cholinesterase inhibitor]] | |||
|indication=[[myasthenia gravis]] | |||
|adverseReactions=[[diaphoresis]], [[diarrhea]], [[excessive salivation]], increased peristalsis, [[nausea and vomiting]], [[stomach cramps]], [[muscle fasciculation]], [[asthenia]], [[miosis]] and excessive [[bronchial secretion]] | |||
|blackBoxWarningTitle=<b><span style="color:#FF0000;">TITLE</span></b> | |||
|blackBoxWarningBody=<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">Condition Name:</span></i> (Content) | |||
|fdaLIADAdult======Myasthenia Gravis===== | |||
Pyridostigmine bromide is available in tablets, each containing 60 mg pyridostigmine bromide. | |||
*Dosage: The size and frequency of the dosage must be adjusted to the needs of the individual patient. The average dose is ten 60-mg tablets daily, spaced to provide maximum relief when maximum strength is needed. In severe cases as many as 25 tablets a day may be required, while in mild cases one to six tablets a day may suffice. | |||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in adult patients. | |||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in adult patients. | |||
|fdaLIADPed======Myasthenia Gravis===== | |||
Pyridostigmine bromide is available in tablets, each containing 60 mg pyridostigmine bromide. | |||
*Dosage: The size and frequency of the dosage must be adjusted to the needs of the individual patient. The average dose is ten 60-mg tablets daily, spaced to provide maximum relief when maximum strength is needed. In severe cases as many as 25 tablets a day may be required, while in mild cases one to six tablets a day may suffice. | |||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in pediatric patients. | |||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in pediatric patients. | |||
|contraindications=Pyridostigmine bromide is contraindicated in mechanical intestinal or [[urinary obstruction]], and particular caution should be used in its administration to patients with [[bronchial asthma]]. Care should be observed in the use of [[atropine]] for counteracting side effects, as discussed below. | |||
|warnings=Although failure of patients to show clinical improvement may reflect underdosage, it can also be indicative of [[overdosage]]. As is true of all [[cholinergic drugs]], overdosage of pyridostigmine bromide may result in [[cholinergic crisis]], a state characterized by increasing [[muscle weakness]] which, through involvement of the muscles of respiration, may lead to death. [[Myasthenic crisis]] due to an increase in the severity of the disease is also accompanied by extreme [[muscle weakness]], and thus may be difficult to distinguish from [[cholinergic crisis]] on a symptomatic basis. Such differentiation is extremely important, since increases in doses of pyridostigmine bromide or other drugs of this class in the presence of cholinergic crisis or of a refractory or "insensitive" state could have grave consequences. Osserman and Genkins indicate that the differential diagnosis of the two types of crisis may require the use of [[Tensilon]] ([[edrophonium chloride]]) as well as clinical judgment. The treatment of the two conditions obviously differs radically. Whereas the presence of myasthenic crisis suggests the need for more intensive anticholinesterase therapy, the diagnosis of cholinergic crisis, according to Osserman and Genkins, calls for the prompt withdrawal of all drugs of this type. The immediate use of [[atropine]] in [[cholinergic crisis]] is also recommended. | |||
[[Atropine]] may also be used to abolish or obtund gastrointestinal side effects or other [[muscarinic]] reactions; but such use, by masking signs of overdosage, can lead to inadvertent induction of [[cholinergic crisis]]. For detailed information on the management of patients with [[myasthenia gravis]], the physician is referred to one of the excellent reviews such as those by Osserman and Genkins, Grob or Schwab. | |||
|clinicalTrials=The side effects of pyridostigmine bromide are most commonly related to overdosage and generally are of two varieties, [[muscarinic]] and [[nicotinic]]. Among those in the former group are [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[diarrhea]], abdominal [[cramps]], increased [[peristalsis]], increased [[salivation]], increased bronchial [[secretions]], [[miosis]] and [[diaphoresis]]. [[Nicotinic]] side effects are comprised chiefly of [[muscle cramps]], [[fasciculation]] and [[weakness]]. [[Muscarinic]] side effects can usually be counteracted by [[atropine]], but for reasons shown in the preceding section the expedient is not without danger. As with any compound containing the [[bromide radical]], a skin [[rash]] may be seen in an occasional patient. Such reactions usually subside promptly upon discontinuance of the medication. | |||
|FDAPregCat=C | |||
|useInPregnancyFDA=The safety of pyridostigmine bromide during pregnancy or lactation in humans has not been established. Therefore, use of pyridostigmine bromide in women who may become pregnant requires weighing the drug's potential benefits against its possible hazards to mother and child. | |||
|AUSPregCat=C | |||
|useInPed=Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. | |||
|administration=*Pyridostigmine bromide is available in tablets, each containing 60 mg pyridostigmine bromide. | |||
|drugBox={{Drugbox2 | |||
| verifiedrevid = 464377022 | |||
| IUPAC_name = 3-[(dimethylcarbamoyl)oxy]-1-methylpyridinium | |||
| image = Pyridostigmine Structure.png | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| tradename = Mestinon | |||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|pyridostigmine-bromide}} | |||
| MedlinePlus = a682229 | |||
| pregnancy_AU = C | |||
| pregnancy_US = C | |||
| legal_UK = POM | |||
| legal_US = Rx-only | |||
| routes_of_administration = Oral, [[Intravenous therapy|intravenous]] | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability = 7.6 +/- 2.4% | |||
| protein_bound = | |||
| metabolism = | |||
| elimination_half-life = 1.78 +/- 0.24hrs | |||
| excretion = [[Kidney|Renal]] | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | |||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 155-97-5 | |||
| ATC_prefix = N07 | |||
| ATC_suffix = AA02 | |||
| ATC_supplemental = | |||
| PubChem = 4991 | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| DrugBank = DB00545 | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 4817 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = 19QM69HH21 | |||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG = D00487 | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEMBL = 1115 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
| C=9 | H=13 | N=2 | O=2 | |||
| molecular_weight = 181.212 g/mol | |||
| smiles = O=C(Oc1ccc[n+](c1)C)N(C)C | |||
| InChI = 1/C9H13N2O2/c1-10(2)9(12)13-8-5-4-6-11(3)7-8/h4-7H,1-3H3/q+1 | |||
| InChIKey = RVOLLAQWKVFTGE-UHFFFAOYAK | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C9H13N2O2/c1-10(2)9(12)13-8-5-4-6-11(3)7-8/h4-7H,1-3H3/q+1 | |||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChIKey = RVOLLAQWKVFTGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
}} | |||
|mechAction=Pyridostigmine bromide inhibits the destruction of acetylcholine by cholinesterase and thereby permits freer transmission of nerve impulses across the neuromuscular junction. | |||
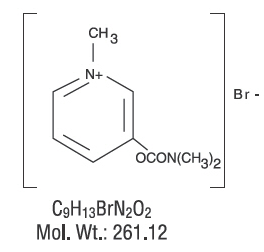
|structure=Chemically, pyridostigmine bromide is 3-hydroxy-1-methylpyridinium bromide dimethylcarbamate. Its structural formula is: | |||
[[file:Pyridostigmine Structure.png|none|450px]] | |||
|PD=Pyridostigmine is an analog of neostigmine (Prostigmin®), but differs from it in certain clinically significant respects; for example, pyridostigmine is characterized by a longer duration of action and fewer gastrointestinal side effects. | |||
|alcohol=Alcohol-Pyridostigmine (patient information) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |||
}} | |||
{{EH}} | {{EH}} | ||
Revision as of 19:20, 14 January 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alberto Plate [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Pyridostigmine (patient information) is a cholinesterase inhibitor that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of myasthenia gravis. Common adverse reactions include diaphoresis, diarrhea, excessive salivation, increased peristalsis, nausea and vomiting, stomach cramps, muscle fasciculation, asthenia, miosis and excessive bronchial secretion.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Myasthenia Gravis
Pyridostigmine bromide is available in tablets, each containing 60 mg pyridostigmine bromide.
- Dosage: The size and frequency of the dosage must be adjusted to the needs of the individual patient. The average dose is ten 60-mg tablets daily, spaced to provide maximum relief when maximum strength is needed. In severe cases as many as 25 tablets a day may be required, while in mild cases one to six tablets a day may suffice.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Myasthenia Gravis
Pyridostigmine bromide is available in tablets, each containing 60 mg pyridostigmine bromide.
- Dosage: The size and frequency of the dosage must be adjusted to the needs of the individual patient. The average dose is ten 60-mg tablets daily, spaced to provide maximum relief when maximum strength is needed. In severe cases as many as 25 tablets a day may be required, while in mild cases one to six tablets a day may suffice.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
Pyridostigmine bromide is contraindicated in mechanical intestinal or urinary obstruction, and particular caution should be used in its administration to patients with bronchial asthma. Care should be observed in the use of atropine for counteracting side effects, as discussed below.
Warnings
Although failure of patients to show clinical improvement may reflect underdosage, it can also be indicative of overdosage. As is true of all cholinergic drugs, overdosage of pyridostigmine bromide may result in cholinergic crisis, a state characterized by increasing muscle weakness which, through involvement of the muscles of respiration, may lead to death. Myasthenic crisis due to an increase in the severity of the disease is also accompanied by extreme muscle weakness, and thus may be difficult to distinguish from cholinergic crisis on a symptomatic basis. Such differentiation is extremely important, since increases in doses of pyridostigmine bromide or other drugs of this class in the presence of cholinergic crisis or of a refractory or "insensitive" state could have grave consequences. Osserman and Genkins indicate that the differential diagnosis of the two types of crisis may require the use of Tensilon (edrophonium chloride) as well as clinical judgment. The treatment of the two conditions obviously differs radically. Whereas the presence of myasthenic crisis suggests the need for more intensive anticholinesterase therapy, the diagnosis of cholinergic crisis, according to Osserman and Genkins, calls for the prompt withdrawal of all drugs of this type. The immediate use of atropine in cholinergic crisis is also recommended.
Atropine may also be used to abolish or obtund gastrointestinal side effects or other muscarinic reactions; but such use, by masking signs of overdosage, can lead to inadvertent induction of cholinergic crisis. For detailed information on the management of patients with myasthenia gravis, the physician is referred to one of the excellent reviews such as those by Osserman and Genkins, Grob or Schwab.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
The side effects of pyridostigmine bromide are most commonly related to overdosage and generally are of two varieties, muscarinic and nicotinic. Among those in the former group are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, increased peristalsis, increased salivation, increased bronchial secretions, miosis and diaphoresis. Nicotinic side effects are comprised chiefly of muscle cramps, fasciculation and weakness. Muscarinic side effects can usually be counteracted by atropine, but for reasons shown in the preceding section the expedient is not without danger. As with any compound containing the bromide radical, a skin rash may be seen in an occasional patient. Such reactions usually subside promptly upon discontinuance of the medication.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): C
The safety of pyridostigmine bromide during pregnancy or lactation in humans has not been established. Therefore, use of pyridostigmine bromide in women who may become pregnant requires weighing the drug's potential benefits against its possible hazards to mother and child.
Pregnancy Category (AUS): C
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Pyridostigmine (patient information) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Pyridostigmine bromide is available in tablets, each containing 60 mg pyridostigmine bromide.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Pyridostigmine (patient information) and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
| |
Pyridostigmine (patient information)
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 3-[(dimethylcarbamoyl)oxy]-1-methylpyridinium | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | N07 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 181.212 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 7.6 +/- 2.4% |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | 1.78 +/- 0.24hrs |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. | |
| Legal status |
POM(UK) [[Prescription drug|Template:Unicode-only]](US) |
| Routes | Oral, intravenous |
Mechanism of Action
Pyridostigmine bromide inhibits the destruction of acetylcholine by cholinesterase and thereby permits freer transmission of nerve impulses across the neuromuscular junction.
Structure
Chemically, pyridostigmine bromide is 3-hydroxy-1-methylpyridinium bromide dimethylcarbamate. Its structural formula is:

Pharmacodynamics
Pyridostigmine is an analog of neostigmine (Prostigmin®), but differs from it in certain clinically significant respects; for example, pyridostigmine is characterized by a longer duration of action and fewer gastrointestinal side effects.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Pyridostigmine (patient information) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Pyridostigmine (patient information) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Pyridostigmine (patient information) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Pyridostigmine (patient information) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [3] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Why is this medication prescribed
Pyridostigmine is used to decrease muscle weakness resulting from myasthenia gravis.
This medication is sometimes prescribed for other uses; ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How should this medicine be used
Pyridostigmine comes as a regular tablet, an extended-release (long-acting) tablet, and a syrup to take by mouth. It usually is taken once, twice, or several times a day, depending on the type of tablet. Your doctor may change your dose, depending on how you respond to the drug. When you first start taking pyridostigmine, your doctor may want you to keep a daily record of the time you take each dose, how long you feel better after taking each dose, and if you have side effects. This record will help the doctor decide how much drug is best for you.
Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take pyridostigmine exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Continue to take pyridostigmine even if you feel well. Do not stop taking pyridostigmine without talking to your doctor.
Pyridostigmine overdose can cause severe illness, including muscle weakness. It is very hard to tell the difference between too little and too much pyridostigmine. Call your doctor immediately if your symptoms become worse.
What special precautions should I follow
Before taking pyridostigmine:
- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to pyridostigmine, bromides, or any other drugs.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications you are taking, especially allergy or cold medications, dexamethasone (Decadron), hydrocortisone (Hydrocortone), magnesium-containing products, medications for heart arrhythmias, sleeping pills, and vitamins.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had intestinal or bladder blockage, asthma, seizures, heart or kidney disease, thyroid problems, or stomach ulcers.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking pyridostigmine, call your doctor.
- you should know that this drug may make you drowsy. Do not drive a car or operate machinery until you know how this drug affects you.
- remember that alcohol can add to the drowsiness caused by this drug.
What special dietary instructions should I follow
Pyridostigmine may cause an upset stomach. Take pyridostigmine with food or milk.
What should I do if I forget a dose
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember it. However, if you remember a missed dose near the time you are supposed to take the next dose, take only the regularly scheduled dose. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one.
Side effects
Mild side effects
Pyridostigmine may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:
- upset stomach
- diarrhea
- vomiting
- drooling
- pale skin
- cold sweats
- blurred vision
- watery eyes
- increased urge to urinate
- anxiousness and feelings of panic
- muscle weakness
Severe side effects
If you experience any of the following symptoms, call your doctor immediately:
- severe itching, skin rash, or hives
- slurred speech
- confusion
- seizures
- difficulty breathing
If you experience a serious side effect, you or your doctor may send a report to the Food and Drug Administration's (FDA) MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program online [at http://www.fda.gov/MedWatch/report.htm] or by phone [1-800-332-1088].
What storage conditions are needed for this medicine
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). Throw away any medication that is outdated or no longer needed. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
In case of emergency/overdose
In case of overdose, call your local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. If the victim has collapsed or is not breathing, call local emergency services at 911.
What other information should I know
Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory. Your doctor will order certain lab tests to check your response to pyridostigmine.
Do not let anyone else take your medication. Ask your pharmacist any questions you have about refilling your prescription.
Brand names
- Mestinon®
- Mestinon® Syrup
- Mestinon® Timespan®