Nabumetone: Difference between revisions
m (Protected "Nabumetone": Protecting pages from unwanted edits ([edit=sysop] (indefinite) [move=sysop] (indefinite))) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage | |||
|authorTag= | |||
{{ | {{VP}} | ||
<!--Overview--> | |||
---- | |||
|genericName= | |||
Nabumetone | |||
|aOrAn= | |||
a | |||
|drugClass= | |||
[[Category: | |indication= | ||
|hasBlackBoxWarning= | |||
Yes | |||
|adverseReactions= | |||
<!--Black Box Warning--> | |||
|blackBoxWarningTitle= | |||
Title | |||
|blackBoxWarningBody= | |||
<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span></i> | |||
* Content | |||
<!--Adult Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | |||
|fdaLIADAdult= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition3===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition4===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Developed by: | |||
* Class of Recommendation: | |||
* Strength of Evidence: | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
|fdaLIADPed= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>FDA-Labeled Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Developed by: | |||
* Class of Recommendation: | |||
* Strength of Evidence: | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Contraindications--> | |||
|contraindications= | |||
* Condition1 | |||
<!--Warnings--> | |||
|warnings= | |||
* Description | |||
====Precautions==== | |||
* Description | |||
<!--Adverse Reactions--> | |||
<!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | |||
|clinicalTrials= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Clinical Trial Experience</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
=====Body as a Whole===== | |||
=====Cardiovascular===== | |||
=====Digestive===== | |||
=====Endocrine===== | |||
=====Hematologic and Lymphatic===== | |||
=====Metabolic and Nutritional===== | |||
=====Musculoskeletal===== | |||
=====Neurologic===== | |||
=====Respiratory===== | |||
=====Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions===== | |||
=====Special Senses===== | |||
=====Urogenital===== | |||
=====Miscellaneous===== | |||
<!--Postmarketing Experience--> | |||
|postmarketing= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Postmarketing Experience</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
=====Body as a Whole===== | |||
=====Cardiovascular===== | |||
=====Digestive===== | |||
=====Endocrine===== | |||
=====Hematologic and Lymphatic===== | |||
=====Metabolic and Nutritional===== | |||
=====Musculoskeletal===== | |||
=====Neurologic===== | |||
=====Respiratory===== | |||
=====Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions===== | |||
=====Special Senses===== | |||
=====Urogenital===== | |||
=====Miscellaneous===== | |||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | |||
|drugInteractions= | |||
* Drug | |||
:* Description | |||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | |||
|useInPregnancyFDA= | |||
* '''Pregnancy Category''' | |||
|useInPregnancyAUS= | |||
* '''Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category''' | |||
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of {{PAGENAME}} in women who are pregnant. | |||
|useInLaborDelivery= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on use of {{PAGENAME}} during labor and delivery. | |||
|useInNursing= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to nursing mothers. | |||
|useInPed= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to pediatric patients. | |||
|useInGeri= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to geriatric patients. | |||
|useInGender= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific gender populations. | |||
|useInRace= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific racial populations. | |||
|useInRenalImpair= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with renal impairment. | |||
|useInHepaticImpair= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with hepatic impairment. | |||
|useInReproPotential= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in women of reproductive potentials and males. | |||
|useInImmunocomp= | |||
There is no FDA guidance one the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients who are immunocompromised. | |||
<!--Administration and Monitoring--> | |||
|administration= | |||
* Oral | |||
* Intravenous | |||
|monitoring= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
* Description | |||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | |||
|IVCompat= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>IV Compatibility</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Overdosage--> | |||
|overdose= | |||
===Acute Overdose=== | |||
====Signs and Symptoms==== | |||
* Description | |||
====Management==== | |||
* Description | |||
===Chronic Overdose=== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Chronic Overdose</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Pharmacology--> | |||
<!--Drug box 2--> | |||
|drugBox= | |||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | |||
|mechAction= | |||
* Nabumetone is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic properties in pharmacologic studies. As with other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, its mode of action is not known. However, the ability to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis may be involved in the anti-inflammatory effect. | |||
<!--Structure--> | |||
|structure= | |||
* Nabumetone is a naphthylalkanone designated chemically as 4-(6-methoxy-2-naphthalenyl)-2-butanone. It has the following structure: | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*Nabumetone is a white to off-white crystalline substance with a molecular weight of 228.3. It is nonacidic and practically insoluble in water, but soluble in alcohol and most organic solvents. It has an n-octanol:phosphate buffer partition coefficient of 2400 at pH 7.4. | |||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | |||
|PD= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Pharmacodynamics</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | |||
|PK= | |||
*After oral administration, approximately 80% of a radiolabeled dose of nabumetone is found in the urine, indicating that nabumetone is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Nabumetone itself is not detected in the plasma because, after absorption, it undergoes rapid biotransformation to the principal active metabolite, 6-methoxy-2-naphthylacetic acid (6MNA). Approximately 35% of a 1000 mg oral dose of nabumetone is converted to 6MNA and 50% is converted into unidentified metabolites which are subsequently excreted in the urine. Following oral administration of nabumetone tablets, 6MNA exhibits pharmacokinetic characteristics that generally follow a one-compartment model with first order input and first order elimination. | |||
*6MNA is more than 99% bound to plasma proteins. The free fraction is dependent on total concentration of 6MNA and is proportional to dose over the range of 1000 mg to 2000 mg. It is 0.2% to 0.3% at concentrations typically achieved following administration of nabumetone 1000 mg and is approximately 0.6% to 0.8% of the total concentrations at steady state following daily administration of 2000 mg. | |||
*Steady-state plasma concentrations of 6MNA are slightly lower than predicted from single-dose data. This may result from the higher fraction of unbound 6MNA which undergoes greater hepatic clearance. | |||
*Co-administration of food increases the rate of absorption and subsequent appearance of 6MNA in the plasma but does not affect the extent of conversion of nabumetone into 6MNA. Peak plasma concentrations of 6MNA are increased by approximately one third. | |||
*Co-administration with an aluminum-containing antacid had no significant effect on the bioavailability of 6MNA. | |||
T1 | |||
*The simulated curves in the graph below illustrate the range of active metabolite plasma concentrations that would be expected from 95% of patients following 1000 mg to 2000 mg doses to steady state. The cross-hatched area represents the expected overlap in plasma concentrations due to intersubject variation following oral administration of 1000 mg to 2000 mg of nabumetone. | |||
*Nabumetone Active Metabolite (6MNA) Plasma Concentrations at Steady State Following Once-Daily Dosing of Nabumetone | |||
*1000 mg (n=31) 2000 mg (n=12) | |||
F1 | |||
*6MNA undergoes biotransformation in the liver, producing inactive metabolites that are eliminated as both free metabolites and conjugates. None of the known metabolites of 6MNA has been detected in plasma. Preliminary in vivo and in vitro studies suggest that unlike other NSAIDs, there is no evidence of enterohepatic recirculation of the active metabolite. Approximately 75% of a radiolabeled dose was recovered in urine in 48 hours. Approximately 80% was recovered in 168 hours. A further 9% appeared in the feces. In the first 48 hours, metabolites consisted of: | |||
1 | |||
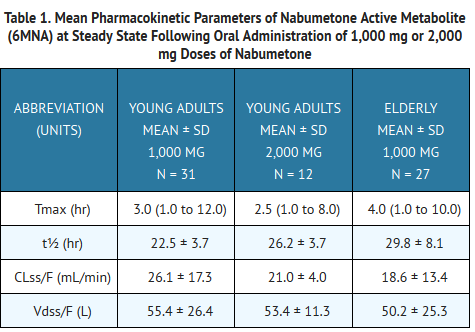
*Following oral administration of dosages of 1000 mg to 2000 mg to steady state, the mean plasma clearance of 6MNA is 20 to 30 mL/min. and the elimination half-life is approximately 24 hours. | |||
*Elderly Patients | |||
:*Steady-state plasma concentrations in elderly patients were generally higher than in young healthy subjects. (See Table 1 for summary of pharmacokinetic parameters.) | |||
*Renal Insufficiency | |||
:*In moderate renal insufficiency patients (creatinine clearance 30 to 49 mL/min), the terminal half-life of 6MNA was increased by approximately 50% (39.2 ± 7.8 hrs, N=12) compared to the normal subjects (26.9 ± 3.3 hrs, N=13), and there was a 50% increase in the plasma levels of unbound 6MNA. | |||
:*Additionally, the renal excretion of 6MNA in the moderate renal impaired patients decreased on average by 33% compared to that in the normal patients. A similar increase in the mean terminal half-life of 6MNA was seen in a small study of patients with severe renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min). In patients undergoing hemodialysis, steady-state plasma concentrations of the active metabolite 6MNA were similar to those observed in healthy subjects. Due to extensive protein binding, 6MNA is not dialyzable. | |||
:*Dosage adjustment of nabumetone generally is not necessary in patients with mild renal insufficiency (≥50 mL/min). Caution should be used in prescribing nabumetone to patients with moderate or severe renal insufficiency. The maximum starting doses of nabumetone in patients with moderate or severe renal insufficiency should not exceed 750 mg or 500 mg, respectively once daily. Following careful monitoring of renal function in patients with moderate or severe renal insufficiency, daily doses may be increased to a maximum of 1,500 mg and 1,000 mg, respectively (see WARNINGS, Renal Effects ). | |||
*Hepatic Impairment | |||
:*Data in patients with severe hepatic impairment are limited. | |||
:*Biotransformation of nabumetone to 6MNA and the further metabolism of 6MNA to inactive metabolites is dependent on hepatic function and could be reduced in patients with severe hepatic impairment (history of or biopsy-proven cirrhosis). | |||
*Special Studies | |||
*Gastrointestinal | |||
:*Nabumetone was compared to aspirin in inducing gastrointestinal blood loss. Food intake was not monitored. Studies utilizing 51Cr-tagged red blood cells in healthy males showed no difference in fecal blood loss after 3 or 4 weeks’ administration of nabumetone 1000 mg or 2000 mg daily when compared to either placebo-treated or nontreated subjects. In contrast, aspirin 3600 mg daily produced an increase in fecal blood loss when compared to the nabumetone-treated, placebo-treated or nontreated subjects. The clinical relevance of the data is unknown. | |||
:*The following endoscopy trials entered patients who had been previously treated with NSAIDs. These patients had varying baseline scores and different courses of treatment. The trials were not designed to correlate symptoms and endoscopy scores. The clinical relevance of these endoscopy trials, i.e., either GI symptoms or serious GI events, is not known. | |||
:*Ten endoscopy studies were conducted in 488 patients who had baseline and post-treatment endoscopy. In 5 clinical trials that compared a total of 194 patients on nabumetone 1000 mg daily or naproxen 250 mg or 500 mg twice daily for 3 to 12 weeks, nabumetone treatment resulted in fewer patients with endoscopically detected lesions (>3 mm). In 2 trials a total of 101 patients on nabumetone 1000 mg or 2000 mg daily or piroxicam 10 mg to 20 mg for 7 to 10 days, there were fewer nabumetone patients with endoscopically detected lesions. In 3 trials of a total of 47 patients on nabumetone 1000 mg daily or indomethacin 100 mg to 150 mg daily for 3 to 4 weeks, the endoscopy scores were higher with indomethacin. Another 12-week trial in a total of 171 patients compared the results of treatment with nabumetone 1000 mg/day to ibuprofen 2400 mg/day and ibuprofen 2400 mg/day plus misoprostol 800 mcg/day. The results showed that patients treated with nabumetone had a lower number of endoscopically detected lesions (>5 mm) than patients treated with ibuprofen alone but comparable to the combination of ibuprofen plus misoprostol. The results did not correlate with abdominal pain. | |||
*Other | |||
:*In 1-week, repeat-dose studies in healthy volunteers, nabumetone 1000 mg daily had little effect on collagen-induced platelet aggregation and no effect on bleeding time. In comparison, naproxen 500 mg daily suppressed collagen-induced platelet aggregation and significantly increased bleeding time. | |||
<!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | |||
|nonClinToxic= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Nonclinical Toxicology</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Clinical Studies--> | |||
|clinicalStudies= | |||
=====Osteoarthritis===== | |||
*The use of nabumetone in relieving the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis (OA) was assessed in double-blind, controlled trials in which 1,047 patients were treated for 6 weeks to 6 months. In these trials, nabumetone in a dose of 1000 mg/day administered at night was comparable to naproxen 500 mg/day and to aspirin 3600 mg/day. | |||
=====Rheumatoid Arthritis===== | |||
*The use of nabumetone in relieving the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was assessed in double-blind, randomized, controlled trials in which 770 patients were treated for 3 weeks to 6 months. Nabumetone, in a dose of 1000 mg/day administered at night was comparable to naproxen 500 mg/day and to aspirin 3600 mg/day. | |||
*In controlled clinical trials of rheumatoid arthritis patients, nabumetone has been used in combination with gold, d-penicillamine and corticosteroids. | |||
======Patient Exposure in Clinical Trials of Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis===== | |||
*In clinical trials with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis patients, most patients responded to nabumetone in doses of 1000 mg/day administered nightly; total daily dosages up to 2000 mg were used. In open-labeled studies, 1,490 patients were permitted dosage increases and were followed for approximately 1 year (mode). Twenty percent of patients (n = 294) were withdrawn for lack of effectiveness during the first year of these open-labeled studies. The following table provides patient exposure to doses used in the U.S. clinical trials: | |||
T2 | |||
*As with other NSAIDs, the lowest dose should be sought for each patient. Patients weighing under 50 kg may be less likely to require dosages beyond 1000 mg. Therefore, after observing the response to initial therapy, the dose should be adjusted to meet individual patients’ requirements. | |||
<!--How Supplied--> | |||
|howSupplied= | |||
* | |||
<!--Patient Counseling Information--> | |||
|fdaPatientInfo= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Patient Counseling Information</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Precautions with Alcohol--> | |||
|alcohol= | |||
* Alcohol-{{PAGENAME}} interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |||
<!--Brand Names--> | |||
|brandNames= | |||
* ®<ref>{{Cite web | title = | url = }}</ref> | |||
<!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | |||
|lookAlike= | |||
* A® — B®<ref name="www.ismp.org">{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = http://www.ismp.org | url = http://www.ismp.org | publisher = | date = }}</ref> | |||
<!--Drug Shortage Status--> | |||
|drugShortage= | |||
}} | |||
<!--Pill Image--> | |||
{{PillImage | |||
|fileName=No image.jpg|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
|drugName= | |||
|NDC= | |||
|drugAuthor= | |||
|ingredients= | |||
|pillImprint= | |||
|dosageValue= | |||
|dosageUnit= | |||
|pillColor= | |||
|pillShape= | |||
|pillSize= | |||
|pillScore= | |||
}} | |||
<!--Label Display Image--> | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}11.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}11.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
<!--Category--> | |||
[[Category:Drug]] | |||
Revision as of 16:31, 21 October 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
Title
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
ConditionName:
|
Overview
Nabumetone is a that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of . There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include .
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition3
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition4
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Nabumetone in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Nabumetone in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Nabumetone in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Nabumetone in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Nabumetone in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Condition1
Warnings
|
Title
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
ConditionName:
|
- Description
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Nabumetone in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Nabumetone in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Nabumetone in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Nabumetone during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nabumetone with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nabumetone with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nabumetone with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nabumetone with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nabumetone with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nabumetone in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nabumetone in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nabumetone in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Nabumetone in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Nabumetone in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Nabumetone in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Nabumetone in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Nabumetone Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- Nabumetone is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic properties in pharmacologic studies. As with other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, its mode of action is not known. However, the ability to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis may be involved in the anti-inflammatory effect.
Structure
- Nabumetone is a naphthylalkanone designated chemically as 4-(6-methoxy-2-naphthalenyl)-2-butanone. It has the following structure:
- Nabumetone is a white to off-white crystalline substance with a molecular weight of 228.3. It is nonacidic and practically insoluble in water, but soluble in alcohol and most organic solvents. It has an n-octanol:phosphate buffer partition coefficient of 2400 at pH 7.4.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Nabumetone in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- After oral administration, approximately 80% of a radiolabeled dose of nabumetone is found in the urine, indicating that nabumetone is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Nabumetone itself is not detected in the plasma because, after absorption, it undergoes rapid biotransformation to the principal active metabolite, 6-methoxy-2-naphthylacetic acid (6MNA). Approximately 35% of a 1000 mg oral dose of nabumetone is converted to 6MNA and 50% is converted into unidentified metabolites which are subsequently excreted in the urine. Following oral administration of nabumetone tablets, 6MNA exhibits pharmacokinetic characteristics that generally follow a one-compartment model with first order input and first order elimination.
- 6MNA is more than 99% bound to plasma proteins. The free fraction is dependent on total concentration of 6MNA and is proportional to dose over the range of 1000 mg to 2000 mg. It is 0.2% to 0.3% at concentrations typically achieved following administration of nabumetone 1000 mg and is approximately 0.6% to 0.8% of the total concentrations at steady state following daily administration of 2000 mg.
- Steady-state plasma concentrations of 6MNA are slightly lower than predicted from single-dose data. This may result from the higher fraction of unbound 6MNA which undergoes greater hepatic clearance.
- Co-administration of food increases the rate of absorption and subsequent appearance of 6MNA in the plasma but does not affect the extent of conversion of nabumetone into 6MNA. Peak plasma concentrations of 6MNA are increased by approximately one third.
- Co-administration with an aluminum-containing antacid had no significant effect on the bioavailability of 6MNA.
T1
- The simulated curves in the graph below illustrate the range of active metabolite plasma concentrations that would be expected from 95% of patients following 1000 mg to 2000 mg doses to steady state. The cross-hatched area represents the expected overlap in plasma concentrations due to intersubject variation following oral administration of 1000 mg to 2000 mg of nabumetone.
- Nabumetone Active Metabolite (6MNA) Plasma Concentrations at Steady State Following Once-Daily Dosing of Nabumetone
- 1000 mg (n=31) 2000 mg (n=12)
F1
- 6MNA undergoes biotransformation in the liver, producing inactive metabolites that are eliminated as both free metabolites and conjugates. None of the known metabolites of 6MNA has been detected in plasma. Preliminary in vivo and in vitro studies suggest that unlike other NSAIDs, there is no evidence of enterohepatic recirculation of the active metabolite. Approximately 75% of a radiolabeled dose was recovered in urine in 48 hours. Approximately 80% was recovered in 168 hours. A further 9% appeared in the feces. In the first 48 hours, metabolites consisted of:
1
- Following oral administration of dosages of 1000 mg to 2000 mg to steady state, the mean plasma clearance of 6MNA is 20 to 30 mL/min. and the elimination half-life is approximately 24 hours.
- Elderly Patients
- Steady-state plasma concentrations in elderly patients were generally higher than in young healthy subjects. (See Table 1 for summary of pharmacokinetic parameters.)
- Renal Insufficiency
- In moderate renal insufficiency patients (creatinine clearance 30 to 49 mL/min), the terminal half-life of 6MNA was increased by approximately 50% (39.2 ± 7.8 hrs, N=12) compared to the normal subjects (26.9 ± 3.3 hrs, N=13), and there was a 50% increase in the plasma levels of unbound 6MNA.
- Additionally, the renal excretion of 6MNA in the moderate renal impaired patients decreased on average by 33% compared to that in the normal patients. A similar increase in the mean terminal half-life of 6MNA was seen in a small study of patients with severe renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min). In patients undergoing hemodialysis, steady-state plasma concentrations of the active metabolite 6MNA were similar to those observed in healthy subjects. Due to extensive protein binding, 6MNA is not dialyzable.
- Dosage adjustment of nabumetone generally is not necessary in patients with mild renal insufficiency (≥50 mL/min). Caution should be used in prescribing nabumetone to patients with moderate or severe renal insufficiency. The maximum starting doses of nabumetone in patients with moderate or severe renal insufficiency should not exceed 750 mg or 500 mg, respectively once daily. Following careful monitoring of renal function in patients with moderate or severe renal insufficiency, daily doses may be increased to a maximum of 1,500 mg and 1,000 mg, respectively (see WARNINGS, Renal Effects ).
- Hepatic Impairment
- Data in patients with severe hepatic impairment are limited.
- Biotransformation of nabumetone to 6MNA and the further metabolism of 6MNA to inactive metabolites is dependent on hepatic function and could be reduced in patients with severe hepatic impairment (history of or biopsy-proven cirrhosis).
- Special Studies
- Gastrointestinal
- Nabumetone was compared to aspirin in inducing gastrointestinal blood loss. Food intake was not monitored. Studies utilizing 51Cr-tagged red blood cells in healthy males showed no difference in fecal blood loss after 3 or 4 weeks’ administration of nabumetone 1000 mg or 2000 mg daily when compared to either placebo-treated or nontreated subjects. In contrast, aspirin 3600 mg daily produced an increase in fecal blood loss when compared to the nabumetone-treated, placebo-treated or nontreated subjects. The clinical relevance of the data is unknown.
- The following endoscopy trials entered patients who had been previously treated with NSAIDs. These patients had varying baseline scores and different courses of treatment. The trials were not designed to correlate symptoms and endoscopy scores. The clinical relevance of these endoscopy trials, i.e., either GI symptoms or serious GI events, is not known.
- Ten endoscopy studies were conducted in 488 patients who had baseline and post-treatment endoscopy. In 5 clinical trials that compared a total of 194 patients on nabumetone 1000 mg daily or naproxen 250 mg or 500 mg twice daily for 3 to 12 weeks, nabumetone treatment resulted in fewer patients with endoscopically detected lesions (>3 mm). In 2 trials a total of 101 patients on nabumetone 1000 mg or 2000 mg daily or piroxicam 10 mg to 20 mg for 7 to 10 days, there were fewer nabumetone patients with endoscopically detected lesions. In 3 trials of a total of 47 patients on nabumetone 1000 mg daily or indomethacin 100 mg to 150 mg daily for 3 to 4 weeks, the endoscopy scores were higher with indomethacin. Another 12-week trial in a total of 171 patients compared the results of treatment with nabumetone 1000 mg/day to ibuprofen 2400 mg/day and ibuprofen 2400 mg/day plus misoprostol 800 mcg/day. The results showed that patients treated with nabumetone had a lower number of endoscopically detected lesions (>5 mm) than patients treated with ibuprofen alone but comparable to the combination of ibuprofen plus misoprostol. The results did not correlate with abdominal pain.
- Other
- In 1-week, repeat-dose studies in healthy volunteers, nabumetone 1000 mg daily had little effect on collagen-induced platelet aggregation and no effect on bleeding time. In comparison, naproxen 500 mg daily suppressed collagen-induced platelet aggregation and significantly increased bleeding time.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Nabumetone in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
Osteoarthritis
- The use of nabumetone in relieving the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis (OA) was assessed in double-blind, controlled trials in which 1,047 patients were treated for 6 weeks to 6 months. In these trials, nabumetone in a dose of 1000 mg/day administered at night was comparable to naproxen 500 mg/day and to aspirin 3600 mg/day.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
- The use of nabumetone in relieving the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was assessed in double-blind, randomized, controlled trials in which 770 patients were treated for 3 weeks to 6 months. Nabumetone, in a dose of 1000 mg/day administered at night was comparable to naproxen 500 mg/day and to aspirin 3600 mg/day.
- In controlled clinical trials of rheumatoid arthritis patients, nabumetone has been used in combination with gold, d-penicillamine and corticosteroids.
=Patient Exposure in Clinical Trials of Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- In clinical trials with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis patients, most patients responded to nabumetone in doses of 1000 mg/day administered nightly; total daily dosages up to 2000 mg were used. In open-labeled studies, 1,490 patients were permitted dosage increases and were followed for approximately 1 year (mode). Twenty percent of patients (n = 294) were withdrawn for lack of effectiveness during the first year of these open-labeled studies. The following table provides patient exposure to doses used in the U.S. clinical trials:
T2
- As with other NSAIDs, the lowest dose should be sought for each patient. Patients weighing under 50 kg may be less likely to require dosages beyond 1000 mg. Therefore, after observing the response to initial therapy, the dose should be adjusted to meet individual patients’ requirements.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Nabumetone Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Nabumetone |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Nabumetone |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Nabumetone in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Nabumetone interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Nabumetone |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Nabumetone |Label Name=Nabumetone11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Nabumetone |Label Name=Nabumetone11.png
}}