Midodrine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
|fdaLIADAdult= | |fdaLIADAdult= | ||
===== | =====Symptomatic Orthostatic Hypotension===== | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :* The recommended dose of midodrine hydrochloride tablets is 10 mg, 3 times daily. | ||
:* Dosing should take place during the daytime hours when the patient needs to be upright, pursuing the activities of daily living. A suggested dosing schedule of approximately 4-hour intervals is as follows: shortly before or upon arising in the morning, midday and late afternoon (not later than 6 P.M.). Doses may be given in 3-hour intervals, if required, to control symptoms, but not more frequently. | |||
:* Single doses as high as 20 mg have been given to patients, but severe and persistent systolic supine hypertension occurs at a high rate (about 45%) at this dose. In order to reduce the potential for supine hypertension during sleep, midodrine hydrochloride tablets should not be given after the evening meal or less than 4 hours before bedtime. Total daily doses greater than 30 mg have been tolerated by some patients, but their safety and usefulness have not been studied systematically or established. Because of the risk of supine hypertension, midodrine hydrochloride tablets should be continued only in patients who appear to attain symptomatic improvement during initial treatment. | |||
:* The supine and standing blood pressure should be monitored regularly and the administration of midodrine hydrochloride tablets should be stopped if supine blood pressure increases excessively. | |||
:* Because desglymidodrine is excreted renally, dosing in patients with abnormal renal function should be cautious; although this has not been systematically studied, it is recommended that treatment of these patients be initiated using 2.5 mg doses. | |||
:* Blood levels of midodrine and desglymidodrine were similar when comparing levels in patients 65 or older vs. younger than 65 and when comparing males vs. females, suggesting dose modifications for these groups are not necessary. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | <!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | ||
| Line 147: | Line 134: | ||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | ||
* Dosing in children has not been adequately studied. | |||
* Dosing | |||
<!--Contraindications--> | <!--Contraindications--> | ||
Revision as of 18:42, 24 July 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* Because midodrine hydrochloride tablets can cause marked elevation of supine blood pressure, it should be used in patients whose lives are considerably impaired despite standard clinical care. The indication for use of midodrine hydrochloride tablets in the treatment of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension is based primarily on a change in a surrogate marker of effectiveness, an increase in systolic blood pressure measured one minute after standing, a surrogate marker considered likely to correspond to a clinical benefit. At present, however, clinical benefits of midodrine hydrochloride tablets, principally improved ability to carry out activities of daily living, have not been verified.
|
Overview
Midodrine is an alpha-adrenergic agonist that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include hypertension, piloerection, pruritus, shivering, paresthesia, dysuria, urinary retention, and urinary frequency.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Symptomatic Orthostatic Hypotension
- Dosing Information
- The recommended dose of midodrine hydrochloride tablets is 10 mg, 3 times daily.
- Dosing should take place during the daytime hours when the patient needs to be upright, pursuing the activities of daily living. A suggested dosing schedule of approximately 4-hour intervals is as follows: shortly before or upon arising in the morning, midday and late afternoon (not later than 6 P.M.). Doses may be given in 3-hour intervals, if required, to control symptoms, but not more frequently.
- Single doses as high as 20 mg have been given to patients, but severe and persistent systolic supine hypertension occurs at a high rate (about 45%) at this dose. In order to reduce the potential for supine hypertension during sleep, midodrine hydrochloride tablets should not be given after the evening meal or less than 4 hours before bedtime. Total daily doses greater than 30 mg have been tolerated by some patients, but their safety and usefulness have not been studied systematically or established. Because of the risk of supine hypertension, midodrine hydrochloride tablets should be continued only in patients who appear to attain symptomatic improvement during initial treatment.
- The supine and standing blood pressure should be monitored regularly and the administration of midodrine hydrochloride tablets should be stopped if supine blood pressure increases excessively.
- Because desglymidodrine is excreted renally, dosing in patients with abnormal renal function should be cautious; although this has not been systematically studied, it is recommended that treatment of these patients be initiated using 2.5 mg doses.
- Blood levels of midodrine and desglymidodrine were similar when comparing levels in patients 65 or older vs. younger than 65 and when comparing males vs. females, suggesting dose modifications for these groups are not necessary.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Midodrine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Midodrine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Midodrine in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Midodrine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
- Dosing in children has not been adequately studied.
Contraindications
- Condition1
Warnings
|
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* Because midodrine hydrochloride tablets can cause marked elevation of supine blood pressure, it should be used in patients whose lives are considerably impaired despite standard clinical care. The indication for use of midodrine hydrochloride tablets in the treatment of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension is based primarily on a change in a surrogate marker of effectiveness, an increase in systolic blood pressure measured one minute after standing, a surrogate marker considered likely to correspond to a clinical benefit. At present, however, clinical benefits of midodrine hydrochloride tablets, principally improved ability to carry out activities of daily living, have not been verified.
|
- Description
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Midodrine in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Midodrine in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Midodrine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Midodrine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Midodrine with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Midodrine with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Midodrine with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Midodrine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Midodrine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Midodrine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Midodrine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Midodrine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Midodrine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Midodrine in the drug label.
Condition1
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Midodrine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Midodrine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Midodrine Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
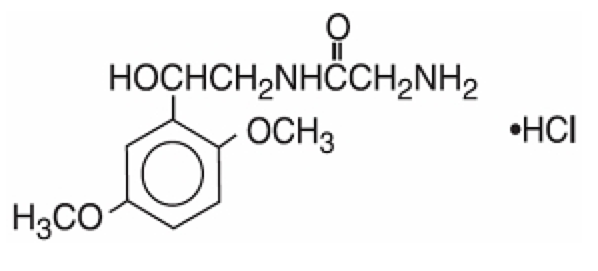
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Midodrine in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Midodrine in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Midodrine in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Midodrine in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Midodrine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Midodrine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Midodrine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Midodrine in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Midodrine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Proamatine®
- Orvaten®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- midodrine — Midrin®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "MIDODRINE HCL (midodrine hydrochloride) tablet".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Midodrine |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Midodrine |Label Name=Midodrine11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Midodrine |Label Name=Midodrine11.png
}}