Macimorelin: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage |authorTag= {{Sonya}} |genericName=generic name |aOrAn=a |drugClass=Acetylcholine release inhibitor, Adrenergic receptor agonist |indicationType=(t...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 225: | Line 225: | ||
(Description regarding monitoring, from ''Warnings'' section) | (Description regarding monitoring, from ''Warnings'' section) | ||
|overdose | |overdose= | ||
*In the event of an overdose, symptomatic and supportive measures should be employed. | |||
|drugBox={{Drugbox2 | |drugBox={{Drugbox2 | ||
| | | ImageFile = Macimorelinwiki.png | ||
| | | ImageAlt = | ||
| | | IUPACName = 2-Amino-''N''-[(2''R'')-1-<nowiki>[[</nowiki>(1''R'')-1-formamido-2-(1''H''-indol-3-yl)ethyl]amino]-3-1''H''-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]-2-methylpropanamide | ||
| OtherNames = Aib-Trp-gTrp-CHO; AEZS-130; JMV 1843; Macimorelin acetate | |||
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| CASNo = 381231-18-1 | |||
| CASNo1 = 945212-59-9 | |||
| CASNo1_Comment = (acetate) | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = 8680B21W73 | |||
| PubChem = 9804938 | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 7980698 | |||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG = D10563 | |||
< | | SMILES = CC(C)(C(=O)N[C@H](CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)N[C@H](CC3=CNC4=CC=CC=C43)NC=O)N | ||
| InChI = 1/C26H30N6O3/c1-26(2,27)25(35)31-22(11-16-13-28-20-9-5-3-7-18(16)20)24(34)32-23(30-15-33)12-17-14-29-21-10-6-4-8-19(17)21/h3-10,13-15,22-23,28-29H,11-12,27H2,1-2H3,(H,30,33)(H,31,35)(H,32,34)/t22-,23-/m1/s1 | |||
| InChIKey = UJVDJAPJQWZRFR-DHIUTWEWBN | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C26H30N6O3/c1-26(2,27)25(35)31-22(11-16-13-28-20-9-5-3-7-18(16)20)24(34)32-23(30-15-33)12-17-14-29-21-10-6-4-8-19(17)21/h3-10,13-15,22-23,28-29H,11-12,27H2,1-2H3,(H,30,33)(H,31,35)(H,32,34)/t22-,23-/m1/s1 | |||
| | | StdInChIKey = UJVDJAPJQWZRFR-DHIUTWEWSA-N}} | ||
|Section2={{Chembox Properties | |||
| C=26 | H=30 | N=6 | O=3 | |||
| | | Appearance = | ||
| | | Density = | ||
| | | MeltingPt = | ||
| | | BoilingPt = | ||
| | | Solubility = }} | ||
| | |Section6={{Chembox Pharmacology | ||
| | | ATCCode_prefix = V04 | ||
| | | ATCCode_suffix = CD06 | ||
| | |||
| ChemSpiderID = | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| KEGG = | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| C= | H= | N= | O= | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
}} | }} | ||
|mechAction= | |Section7={{Chembox Hazards | ||
|structure= | | MainHazards = | ||
|PD=( | | FlashPt = | ||
|PK= | | AutoignitionPt = }} | ||
}} | |||
|mechAction= | |||
*Macimorelin stimulates GH release by activating growth hormone secretagogue receptors present in the pituitary and hypothalamus. | |||
( | |structure= | ||
[[image:macimorelinstructure.png|none|thumb|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
===== | |PD= | ||
=====GH stimulation===== | |||
*Maximum GH levels are observed between 30 to 90 minutes after administration of MACRILEN. | |||
=====Cardiac electrophysiology===== | |||
===== | *The effects of macimorelin on ECG parameters were investigated in a dedicated Thorough QT study that investigated in a 3-way cross-over design with 60 healthy subjects the effects of a supra-therapeutic dose of macimorelin (2 mg/kg) (4 times the recommended dosage) in comparison with placebo and with moxifloxacin. This study showed a mean baseline- and placebo-adjusted change (upper single-sided 95% confidence interval) in QTcF of 9.6 msec (11.4 msec) at 4 h post-dose, which occurred after the mean maximum macimorelin plasma concentration (0.5 h). A similar increase in the QTcF interval was also observed in a single-ascending dose study, which included three dose levels (0.5 mg/kg, and 1 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg (2 times and 4 times the recommended dosage, respectively). All three doses levels studied showed a similar magnitude of QTcF prolongation in the Thorough QT study, suggesting an absence of dose dependent changes. The mechanism for the observed QTcF prolongation is unknown. | ||
|PK= | |||
( | *The mean plasma macimorelin concentrations are similar between patients with AGHD and healthy subjects for 1.5 hours following administration of a single oral dose of 0.5 mg macimorelin/kg body weight. | ||
=====Absorption===== | |||
*The maximum plasma macimorelin concentrations (C<sub>max</sub>) were observed between 0.5 hour and 1.5 hours following oral administration of 0.5 mg macimorelin/kg body weight to patients with AGHD under fasting for at least 8 hours. A liquid meal decreased the macimorelin C<sub>max</sub> and AUC by 55% and 49%, respectively. | |||
=====Elimination===== | |||
*An in vitro human liver microsomes study showed that CYP3A4 is the major enzyme to metabolize macimorelin. | |||
| | *Macimorelin was eliminated with a mean terminal half-life (T<sub>1/2</sub>) of 4.1 hours following administration of a single oral dose of 0.5 mg macimorelin/kg body weight in healthy subjects. | ||
|nonClinToxic= | |||
* ( | =====Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility===== | ||
* ( | =====Carcinogenesis===== | ||
*Long-term carcinogenesis studies in rodents have not been conducted. | |||
=====Mutagenesis===== | |||
*Macimorelin did not cause mutations in bacteria under assay conditions with or without metabolic activation. There were also no mutations or clastogenic effects in mouse lymphoma cells with or without metabolic activation. | |||
=====Impairment of Fertility===== | |||
*No studies have been conducted to assess the effect of macimorelin on fertility. | |||
|clinicalStudies= | |||
*The diagnostic efficacy of the MACRILEN test was established in a randomized, open-label, single-dose, cross-over study. The objective of the study was to compare the level of agreement between MACRILEN test results and insulin tolerance test (ITT) results in adult patients with different pre-test probability of growth hormone deficiency and healthy control subjects. The four groups of individuals evaluated were: | |||
:*Group A: Adults with a high likelihood of growth hormone deficiency (GHD) | |||
::*Structural hypothalamic or pituitary lesions and low insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and/or | |||
::*Three or more pituitary hormone deficiencies and low IGF-1, or | |||
::*Childhood onset GHD with structural lesions and low IGF-1. | |||
:*Group B: Adults with an intermediate likelihood of GHD | |||
::*Eligible subjects not qualifying for either high or low likelihood. | |||
:*Group C: Adults with a low likelihood of GHD | |||
::*One risk factor for GHD only, such as history of distant traumatic brain injury or one pituitary hormone deficiency only with otherwise normal pituitary function, or | |||
::*Isolated idiopathic childhood onset GHD without additional pituitary deficits. | |||
:*Group D: Healthy adult controls | |||
::*Healthy subjects matching Group A subjects by sex, age ± 5 years, body mass index (BMI ± 2 kg/m<sup>2</sup>), and estrogen status (females only). | |||
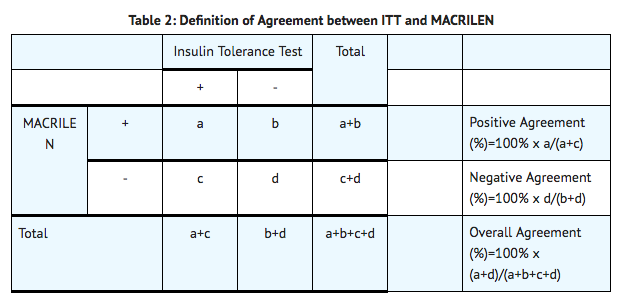
*For both the ITT and the MACRILEN test, serum concentrations of growth hormone were measured at 30, 45, 60, and 90 minutes after drug administration. The test was considered positive (i.e., growth hormone deficiency diagnosed) if the maximum serum GH level observed after stimulation was less than the pre-specified cut point value of 2.8 ng/mL for the MACRILEN test or 5.1 ng/mL for the ITT. | |||
*The level of negative and positive agreement between the results of the ITT and the MACRILEN test was used to evaluate the performance of the MACRILEN test. In the study, the ITT is used as the benchmark (i.e., a negative ITT indicates absence of disease and a positive ITT indicates presence of disease). Negative agreement is the proportion of subjects with a negative ITT (i.e., those who do not have GHD per the ITT) who also have a negative MACRILEN test. With a high level of negative agreement, the MACRILEN test will not wrongly diagnose an individual without GHD per the ITT as having GHD. Positive agreement is the proportion of subjects with a positive ITT (i.e., those who have GHD per the ITT) who also have a positive MACRILEN test. With a high level of positive agreement, the MACRILEN test will not wrongly diagnose an individual with GHD per the ITT as not having GHD. The agreement measures are defined mathematically below. | |||
[[image:macimorelintrial1.png|none|thumb|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
=====Results===== | |||
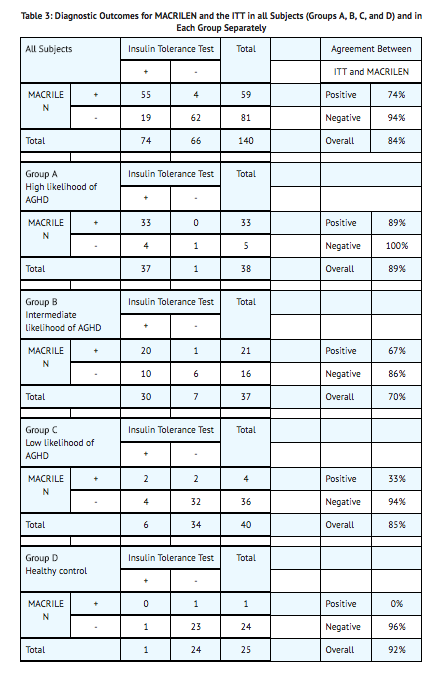
*One hundred and fifty-seven subjects underwent at least one of the two tests in this study, 59% were male, 41% female, and 86% of white origin. The median age was 41 years (range: 18 – 66 years) and body mass index 27.5 kg/m<sup>2</sup> (range: 16 – 40 kg/m2). The study relied on a cross-over design and each participant was to undergo the two diagnostic tests and serve as his or her own control. Data on both tests were available for 140 subjects; 38 (27%) in Group A, 37 (26%) in Group B, 40 (29%) in Group C, and 25 (18%) in Group D. One out of 154 MACRILEN tests (0.6%) performed failed due to a technical error and 27 out of 157 ITTs (17.2%) performed failed because induction of severe hypoglycemia (i.e., the stimulus) could not be achieved. | |||
*Two-by-two tables presenting the pre-specified primary analysis results for the ITT and MACRILEN test are shown below for all subjects (Groups A, B, C, and D combined) and for each group separately. The estimates for negative and positive agreement between MACRILEN and the ITT in the overall study population were 94% and 74% with lower 95% confidence interval bounds 85% and 63%, respectively. Negative and positive agreement between MACRILEN and the ITT in subjects with intermediate or low risk (Groups B and C) were 93% and 61% with lower 95% confidence interval bounds 80% and 43%, respectively. These results are based on peak GH values (maximum GH concentrations across all measurement timepoints). | |||
[[image:macimorelintrial2.png|none|thumb|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*Repeatability was tested in a subset of 34 subjects who underwent two MACRILEN tests. Agreement between the result of the first test and the second test was observed in 31 cases (91.2%). | |||
|howSupplied= | |||
*MACRILEN 60 mg is supplied as white to off-white granules in an aluminum pouch. Each pouch contains 60 mg macimorelin (equivalent to 68 mg macimorelin acetate) that when reconstituted with 120 mL of water provides a 60 mg/120 mL (0.5 mg/mL) macimorelin solution. | |||
*MACRILEN is available in boxes containing 1 pouch per box (NDC 71090-002-02). | |||
*Before administration, MACRILEN for oral solution must be reconstituted by a healthcare professional. | |||
|storage= | |||
*Store pouches under refrigeration at 2-8°C (36-46°F). | |||
*The solution must be used within 30 minutes after preparation. Discard unused portion. | |||
|packLabel= | |||
[[image:macimorelinlabel1.jpeg|none|thumb|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
[[image:macimorelinlabel2.jpeg|none|thumb|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
|fdaPatientInfo= | |||
*Instruct patients to discontinue treatment with GH at least one week before administering MACRILEN. Also, instruct patients to discontinue other medications that may interfere with the diagnostic test results prior to MACRILEN administration. | |||
*Instruct patients to fast for at least 8 hours before MACRILEN administration | |||
|nlmPatientInfo= | |||
|lookAlike= | |||
|brandNames= | |brandNames= | ||
*Macrilen | |||
|drugShortage=Drug Shortage | |drugShortage=Drug Shortage | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 18:46, 18 July 2018
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sonya Gelfand
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
Warning Title
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
Condition Name: (Content)
|
Overview
Macimorelin is a Acetylcholine release inhibitor, Adrenergic receptor agonist that is FDA approved for the (type of indication of drug) of a list of indications, separated by commas.. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include a list of adverse reactions, separated by commas..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Contraindications
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Warnings
|
Warning Title
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
Condition Name: (Content)
|
Conidition 1
(Description)
Conidition 2
(Description)
Conidition 3
(Description)
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Condition 2
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Postmarketing Experience
(Description)
Drug Interactions
- Drug 1
- Drug 2
- Drug 3
- Drug 4
- Drug 5
Drug 1
(Description)
Drug 2
(Description)
Drug 3
(Description)
Drug 4
(Description)
Drug 5
(Description)
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
(Description)
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Macimorelin in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
(Description)
Nursing Mothers
(Description)g
Pediatric Use
(Description)
Geriatic Use
(Description)
Gender
(Description)
Race
(Description)
Renal Impairment
(Description)
Hepatic Impairment
(Description)
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
(Description)
Immunocompromised Patients
(Description)
Others
(Description)
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
(Oral/Intravenous/etc)
Monitoring
Condition 1
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Macimorelin and IV administrations.
Overdosage
- In the event of an overdose, symptomatic and supportive measures should be employed.
Pharmacology
Macimorelin
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
- Macimorelin stimulates GH release by activating growth hormone secretagogue receptors present in the pituitary and hypothalamus.
Structure
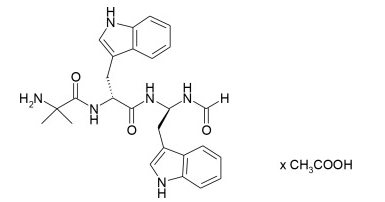
Pharmacodynamics
GH stimulation
- Maximum GH levels are observed between 30 to 90 minutes after administration of MACRILEN.
Cardiac electrophysiology
- The effects of macimorelin on ECG parameters were investigated in a dedicated Thorough QT study that investigated in a 3-way cross-over design with 60 healthy subjects the effects of a supra-therapeutic dose of macimorelin (2 mg/kg) (4 times the recommended dosage) in comparison with placebo and with moxifloxacin. This study showed a mean baseline- and placebo-adjusted change (upper single-sided 95% confidence interval) in QTcF of 9.6 msec (11.4 msec) at 4 h post-dose, which occurred after the mean maximum macimorelin plasma concentration (0.5 h). A similar increase in the QTcF interval was also observed in a single-ascending dose study, which included three dose levels (0.5 mg/kg, and 1 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg (2 times and 4 times the recommended dosage, respectively). All three doses levels studied showed a similar magnitude of QTcF prolongation in the Thorough QT study, suggesting an absence of dose dependent changes. The mechanism for the observed QTcF prolongation is unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
- The mean plasma macimorelin concentrations are similar between patients with AGHD and healthy subjects for 1.5 hours following administration of a single oral dose of 0.5 mg macimorelin/kg body weight.
Absorption
- The maximum plasma macimorelin concentrations (Cmax) were observed between 0.5 hour and 1.5 hours following oral administration of 0.5 mg macimorelin/kg body weight to patients with AGHD under fasting for at least 8 hours. A liquid meal decreased the macimorelin Cmax and AUC by 55% and 49%, respectively.
Elimination
- An in vitro human liver microsomes study showed that CYP3A4 is the major enzyme to metabolize macimorelin.
- Macimorelin was eliminated with a mean terminal half-life (T1/2) of 4.1 hours following administration of a single oral dose of 0.5 mg macimorelin/kg body weight in healthy subjects.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
- Long-term carcinogenesis studies in rodents have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
- Macimorelin did not cause mutations in bacteria under assay conditions with or without metabolic activation. There were also no mutations or clastogenic effects in mouse lymphoma cells with or without metabolic activation.
Impairment of Fertility
- No studies have been conducted to assess the effect of macimorelin on fertility.
Clinical Studies
- The diagnostic efficacy of the MACRILEN test was established in a randomized, open-label, single-dose, cross-over study. The objective of the study was to compare the level of agreement between MACRILEN test results and insulin tolerance test (ITT) results in adult patients with different pre-test probability of growth hormone deficiency and healthy control subjects. The four groups of individuals evaluated were:
- Group A: Adults with a high likelihood of growth hormone deficiency (GHD)
- Structural hypothalamic or pituitary lesions and low insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and/or
- Three or more pituitary hormone deficiencies and low IGF-1, or
- Childhood onset GHD with structural lesions and low IGF-1.
- Group B: Adults with an intermediate likelihood of GHD
- Eligible subjects not qualifying for either high or low likelihood.
- Group C: Adults with a low likelihood of GHD
- One risk factor for GHD only, such as history of distant traumatic brain injury or one pituitary hormone deficiency only with otherwise normal pituitary function, or
- Isolated idiopathic childhood onset GHD without additional pituitary deficits.
- Group D: Healthy adult controls
- Healthy subjects matching Group A subjects by sex, age ± 5 years, body mass index (BMI ± 2 kg/m2), and estrogen status (females only).
- For both the ITT and the MACRILEN test, serum concentrations of growth hormone were measured at 30, 45, 60, and 90 minutes after drug administration. The test was considered positive (i.e., growth hormone deficiency diagnosed) if the maximum serum GH level observed after stimulation was less than the pre-specified cut point value of 2.8 ng/mL for the MACRILEN test or 5.1 ng/mL for the ITT.
- The level of negative and positive agreement between the results of the ITT and the MACRILEN test was used to evaluate the performance of the MACRILEN test. In the study, the ITT is used as the benchmark (i.e., a negative ITT indicates absence of disease and a positive ITT indicates presence of disease). Negative agreement is the proportion of subjects with a negative ITT (i.e., those who do not have GHD per the ITT) who also have a negative MACRILEN test. With a high level of negative agreement, the MACRILEN test will not wrongly diagnose an individual without GHD per the ITT as having GHD. Positive agreement is the proportion of subjects with a positive ITT (i.e., those who have GHD per the ITT) who also have a positive MACRILEN test. With a high level of positive agreement, the MACRILEN test will not wrongly diagnose an individual with GHD per the ITT as not having GHD. The agreement measures are defined mathematically below.
Results
- One hundred and fifty-seven subjects underwent at least one of the two tests in this study, 59% were male, 41% female, and 86% of white origin. The median age was 41 years (range: 18 – 66 years) and body mass index 27.5 kg/m2 (range: 16 – 40 kg/m2). The study relied on a cross-over design and each participant was to undergo the two diagnostic tests and serve as his or her own control. Data on both tests were available for 140 subjects; 38 (27%) in Group A, 37 (26%) in Group B, 40 (29%) in Group C, and 25 (18%) in Group D. One out of 154 MACRILEN tests (0.6%) performed failed due to a technical error and 27 out of 157 ITTs (17.2%) performed failed because induction of severe hypoglycemia (i.e., the stimulus) could not be achieved.
- Two-by-two tables presenting the pre-specified primary analysis results for the ITT and MACRILEN test are shown below for all subjects (Groups A, B, C, and D combined) and for each group separately. The estimates for negative and positive agreement between MACRILEN and the ITT in the overall study population were 94% and 74% with lower 95% confidence interval bounds 85% and 63%, respectively. Negative and positive agreement between MACRILEN and the ITT in subjects with intermediate or low risk (Groups B and C) were 93% and 61% with lower 95% confidence interval bounds 80% and 43%, respectively. These results are based on peak GH values (maximum GH concentrations across all measurement timepoints).
- Repeatability was tested in a subset of 34 subjects who underwent two MACRILEN tests. Agreement between the result of the first test and the second test was observed in 31 cases (91.2%).
How Supplied
- MACRILEN 60 mg is supplied as white to off-white granules in an aluminum pouch. Each pouch contains 60 mg macimorelin (equivalent to 68 mg macimorelin acetate) that when reconstituted with 120 mL of water provides a 60 mg/120 mL (0.5 mg/mL) macimorelin solution.
- MACRILEN is available in boxes containing 1 pouch per box (NDC 71090-002-02).
- Before administration, MACRILEN for oral solution must be reconstituted by a healthcare professional.
Storage
- Store pouches under refrigeration at 2-8°C (36-46°F).
- The solution must be used within 30 minutes after preparation. Discard unused portion.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Macimorelin |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel


{{#ask: Label Page::Macimorelin |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Instruct patients to discontinue treatment with GH at least one week before administering MACRILEN. Also, instruct patients to discontinue other medications that may interfere with the diagnostic test results prior to MACRILEN administration.
- Instruct patients to fast for at least 8 hours before MACRILEN administration
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Macimorelin interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Macrilen
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Macimorelin Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.