Isoproterenol (injection)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | inhaled 80-120μg |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
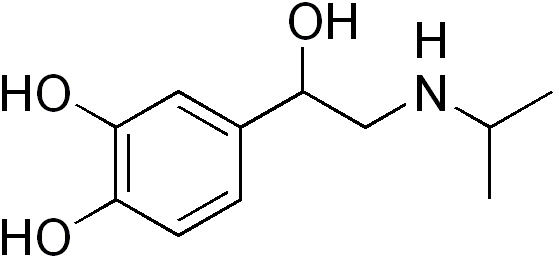
| Formula | C11H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 211.258 g/mol |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Isoproterenol hydrochloride or isoprenaline (Medihaler-Iso®) is a sympathomimetic beta adrenergic receptor agonist medication.
It is structurally similar to epinephrine but acts for the most part on beta receptors.
Uses
It is used as an inhaled aerosol to treat asthma. Although it activates all beta adrenergic receptors, it works in a similar fashion to the more selective beta2-adrenergic receptor agonists e.g. salbutamol, by relaxing the airways to increase airflow.
It is also supplied in ampules under the brand name Isuprel® for injection and in sublingual pill form for treatment of asthma, chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Used with caution, it can also be used to treat torsades de pointes, in conjunction with overdrive pacing and magnesium.
Pharmacology
Isoproterenol is a β1- and β2-adrenoceptor agonist which was commonly used to treat asthma before the more widespread use of salbutamol, which has more selective effects on the airways. Its route of administration is either intravenous, oral, intranasal, subcutaneous, or intramuscular, depending on use. The plasma half-life for isoproterenol is approximately two hours.
Isoproterenol's effects on the cardiovascular system relate to its actions on cardiac β1 receptors and β2 receptors on skeletal muscle arterioles. Isoproterenol has positive inotropic and chronotropic effects on the heart. In skeletal muscle arterioles it produces vasodilatation. Its inotropic and chronotropic effects elevate systolic blood pressure, while its vasodilatory effects tend to lower diastolic blood pressure.
The adverse effects of isoproterenol are also related to the drug's cardiovascular effects. Isoproterenol can produce an elevated heart rate (tachycardia), which predisposes patients to cardiac dysrhythmias.
Warnings and Contraindications
Isoproterenol should not be administered to patients with myocardial ischaemia.
Template:Adrenergic and dopaminergic agents
- Pages with script errors
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Antiasthmatic drugs
- Phenethylamines
- Drugs