Infectious disease transmission
|
Infectious disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Infectious disease transmission On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Infectious disease transmission |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Infectious disease transmission |
Please help WikiDoc by adding more content here. It's easy! Click here to learn about editing.
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [2]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [3]
Transmission
An infectious disease is transmitted from some source. Defining the means of transmission plays an important part in understanding the biology of an infectious agent, and in addressing the disease it causes. Transmission may occur through several different mechanisms. Respiratory diseases and meningitis are commonly acquired by contact with aerosolized droplets, spread by sneezing, coughing, talking or even singing. Gastrointestinal diseases are often acquired by ingesting contaminated food and water. Sexually transmitted diseases are acquired through contact with bodily fluids, generally as a result of sexual activity. Some infectious agents may be spread as a result of contact with a contaminated, inanimate object (known as a fomite), such as a coin passed from one person to another, while other diseases penetrate the skin directly.
Transmission of infectious diseases may also involve a "vector". Vectors may be mechanical or biological. A mechanical vector picks up an infectious agent on the outside of its body and transmits it in a passive manner. An example of a mechanical vector is a housefly, which lands on cow dung, contaminating its appendages with bacteria from the feces, and then lands on food prior to consumption. The pathogen never enters the body of the fly.
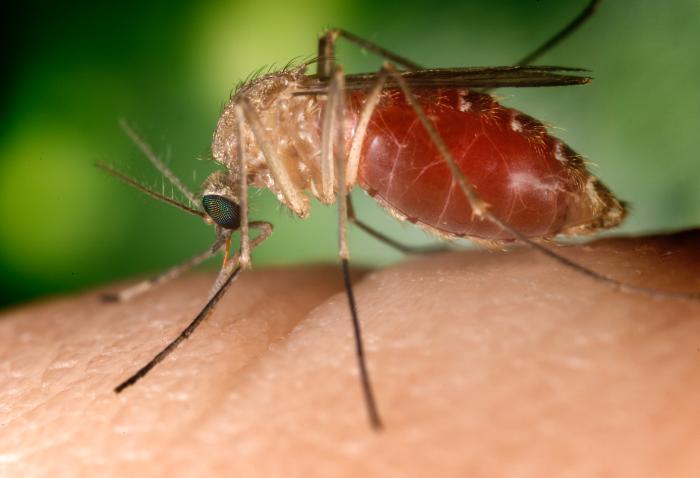
In contrast, biological vectors harbor pathogens within their bodies and deliver pathogens to new hosts in an active manner, usually a bite. Biological vectors are often responsible for serious blood-borne diseases, such as malaria,viral encephalitis, Chagas disease and African sleeping sickness. Biological vectors are usually, though not exclusively, arthropods, such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas and lice. Vectors are often required in the life cycle of a pathogen. A common strategy, used to control vector borne infectious diseases, is to interrupt the life cycle of a pathogen, by killing the vector.
The relationship between virulence and transmission is complex, and has important consequences for the long term evolution of a pathogen. Since it takes time for a microbe and a new host species to co-evolve, an emerging pathogen may hit its earliest victims especially hard. It is usually in the first wave of a new disease that death rates are highest. If a disease is rapidly fatal, the host may die before the microbe can get passed along to another host. However, this cost may be overwhelmed by the short term benefit of higher infectiousness if transmission is linked to virulence, as it is for instance in the case of cholera (the explosive diarrhea aids the bacterium in finding new hosts) or many respiratory infections (sneezing and coughing create infectious aerosols).