Hymenolepis infection laboratory findings
Overview
The diagnosis depends on the demonstration of eggs in stool specimens. Concentration techniques and repeated examinations will increase the likelihood of detecting light infections.
Laboratory Findings
Microscopy:
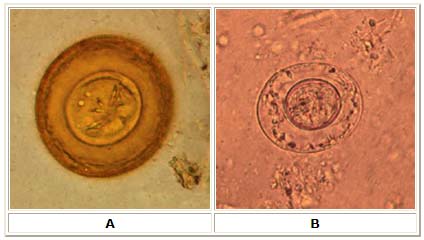
A: Egg of Hymenolepis diminuta. These eggs are round or slightly oval, size 70 to 86 µm by 60 to 80 µm, with a striated outer membrane and a thin inner membrane. The space between the membranes is smooth or faintly granular. The oncosphere has six hooks (of which at least four are visible at this level of focus). Image contributed by Georgia Department of Public Health.
B: Egg of Hymenolepis nana. These eggs are oval and smaller than those of H. diminuta, their size being 30 to 55 µm. On the inner membrane are two poles, from which 4 to 8 polar filaments spread out between the two membranes. The oncosphere has six hooks (seen as dark lines at 8 o'clock). Image contributed by Georgia Department of Public Health.
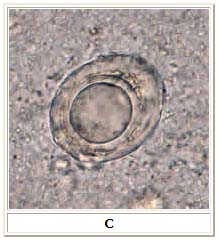
C: Artifact resembling a H. nana egg. However, no hooks and no polar filaments are visible in the artifact.
Macroscopic:
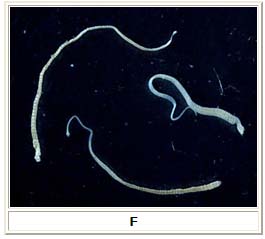
F: Three adult Hymenolepis nana tapeworms. Each tapeworm (length: 15 to 40 mm) has a small, rounded scolex at the anterior end, and proglottids can be distinguished at the posterior, wider end. Image contributed by the Georgia Division of Public Health.