Arabinose
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Arabinose is an aldopentose — a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including an aldehyde (CHO) functional group. It has chemical formula C5H10O5 and a molar mass of 150.13 g/mol.
Isomerism
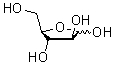
For biosynthetic reasons, saccharides are almost always more abundant in nature as the "D" form, or structurally analogous to D-(+)-glyceraldehyde.[1] However, L-arabinose is in fact more common than D-arabinose in nature and is found in nature as a component of biopolymers such as hemicellulose and pectin. The L-arabinose operon is a very important operon in molecular biology and bioengineering.
A classic method for the organic synthesis of arabinose from glucose is the Wohl degradation.
References
- ↑ For sugars, the D/L nomenclature does not refer to the molecule's optical rotation properties.
See also
de:Arabinose eo:Arabinozo it:Arabinosio he:אראבינוז nl:Arabinose fi:Arabinoosi