Activated protein C resistance
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
Activated protein C resistance is a hemostatic disorder characterized by a poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C (APC). This results in an increased risk of venous thrombosis.
Activated protein C (with protein S as a cofactor) degrades Factor Va and Factor VIIIa. Activated protein C resistance is the inability of protein C to cleave Factor Va and/or Factor VIIIa, which allows for longer duration of thrombin generation and may lead to a hypercoagulable state. This may be hereditary or acquired. The best known and most common hereditary form is Factor V Leiden. Acquired forms occur in the presence of elevated Factor VIII concentrations.
It has been estimated that up to 64% of patients with venous thromboembolism might have activated protein C resistance.
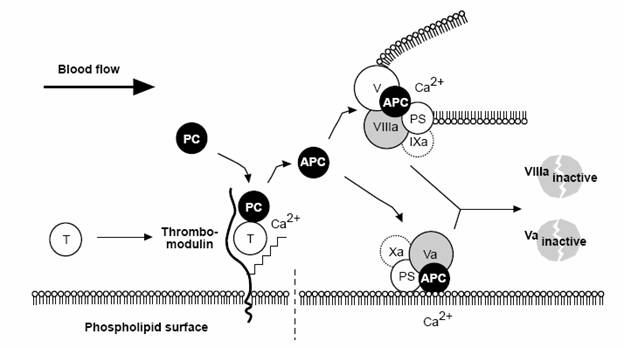
Figure: The Protein C Anticoagulant Pathway: Thrombin escaping from a site of vascular injury binds to its receptor thrombomodulin (TM) on the intact cell surface. As a result, thrombin loses its procoagulant properties and instead becomes a potent activator of protein C. Activated protein C (APC) functions as a circulating anticoagulant, which specifically degrades and inactivates the phospholipid-bound factors Va and VIIIa. This effectively down-regulates the coagulation cascade and limits clot formation to sites of vascular injury. T = Thrombin, PC= Protein C, Activated Protein C= APC, PS= Protein S
References
- Nicolaes GA, Dahlback B (2003). "Congenital and acquired activated protein C resistance". Semin Vasc Med. 3 (1): 33–46. PMID 15199491
- Dahlback B (2003). "The discovery of activated protein C resistance". J Thromb Haemost. 1 (1): 3–9. PMID 12871530
- Sheppard DR (2000). "Activated protein C resistance: the most common risk factor for venous thromboembolism". J Am Board Fam Pract. 13 (2): 111–5. PMID 10764192