21-hydroxylase deficiency pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
==Microscopic Pathology== | ==Microscopic Pathology== | ||
In | In 21 hydroxylase deficiency microscopic findings may include: | ||
* Diffuse cortical hyperplasia with smaller cells | |||
* The cell cytoplasm can be vacuolated, and often more basophilic. | |||
* Rare mitotic figures may be present | |||
* The hyperplastic cells typically lack features of cellular atypia.<ref name="urlAdrenal Gland - Hyperplasia - Nonneoplastic Lesion Atlas">{{cite web |url=https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/nnl/endocrine/adrenal/hyperpl/index.htm |title=Adrenal Gland - Hyperplasia - Nonneoplastic Lesion Atlas |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | |||
{| | {| | ||
| | | | ||
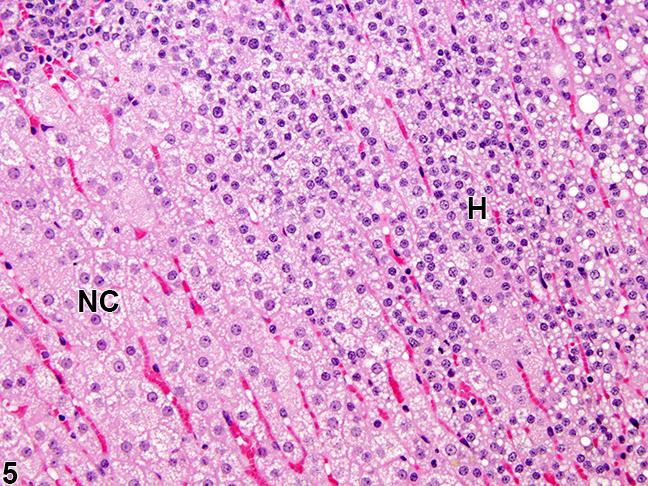
[[Image:Cah mic.jpg|thumb|200px|frame|Adrenal gland, Cortex - Hyperplasia in a female rat from a chronic study. There is a hyperplastic lesion (H) in which cortical cells are increased in number but are smaller in size than adjacent normal cortical cells (NC) | [[Image:Cah mic.jpg|thumb|200px|frame|Adrenal gland, Cortex - Hyperplasia in a female rat from a chronic study. There is a hyperplastic lesion (H) in which cortical cells are increased in number but are smaller in size than adjacent normal cortical cells (NC)<ref name="urlAdrenal Gland - Hyperplasia - Nonneoplastic Lesion Atlas">{{cite web |url=https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/nnl/endocrine/adrenal/hyperpl/index.htm |title=Adrenal Gland - Hyperplasia - Nonneoplastic Lesion Atlas |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | ||
| | | | ||
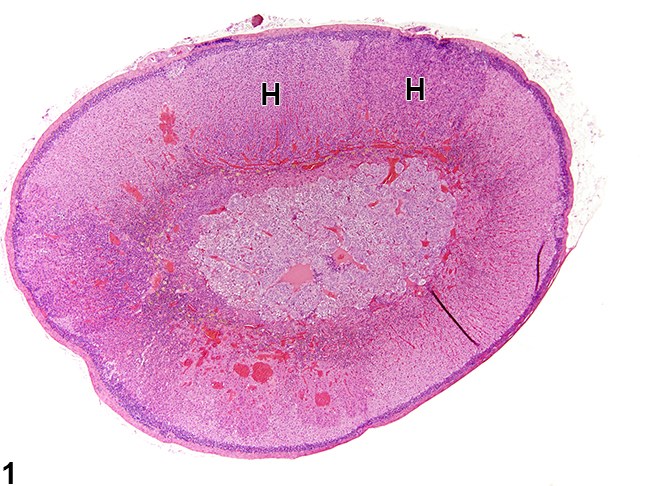
[[Image:Cah.jpg|thumb|250px|frame|Adrenal gland, Cortex - Hyperplasia in a male rat from a chronic study. There are two adjacent foci of hyperplasia (H) in the zona fasciculata. | [[Image:Cah.jpg|thumb|250px|frame|Adrenal gland, Cortex - Hyperplasia in a male rat from a chronic study. There are two adjacent foci of hyperplasia (H) in the zona fasciculata.<ref name="urlAdrenal Gland - Hyperplasia - Nonneoplastic Lesion Atlas">{{cite web |url=https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/nnl/endocrine/adrenal/hyperpl/index.htm |title=Adrenal Gland - Hyperplasia - Nonneoplastic Lesion Atlas |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 18:53, 2 August 2017
|
21-hydroxylase deficiency Microchapters |
|
Differentiating 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency from other Diseases |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
21-hydroxylase deficiency pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of 21-hydroxylase deficiency pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for 21-hydroxylase deficiency pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Mehrian Jafarizade, M.D [2]
Overview
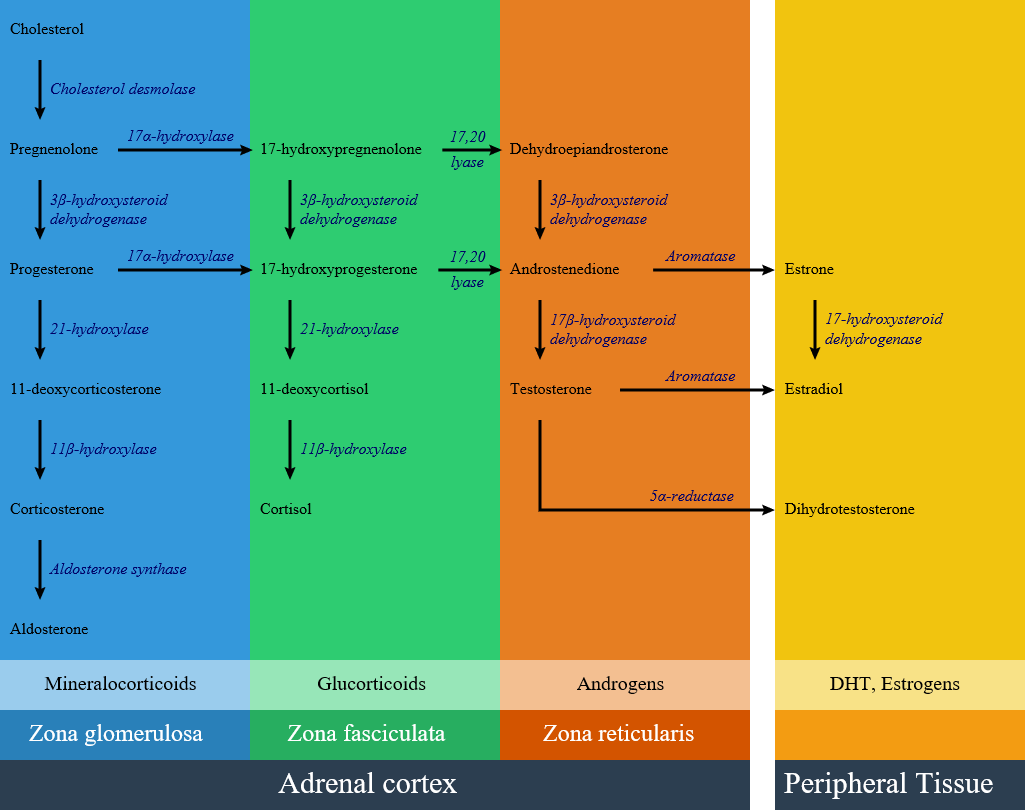
In patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency, there is a defective conversion of 17-hydroxyprogesterone to 11-deoxycortisol which results in decreased cortisol synthesis and therefore increased corticotropin (ACTH) secretion. The resulting adrenal stimulation leads to increased production of androgens. More than 95% of all cases of CAH are caused by 21-hydroxylase deficiency. The clinical manifestation of congenital adrenal hyperplasia is closely related to the type and severity of disease. The severity of disease relates to the mutation type which is caused enzyme inactivity or hypo activity. There is a lack of enzyme in classic type of 21-hydroxylase deficiency; while in the non-classic form, enzymatic activity is reduced but sufficient to maintain normal glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid production. Responsible gene for 21-hydroxylase deficiency is CYP21A. This gene is located within the human leucocyte antigen class III region of chromosome 6. Meiotic recombination events occurs in this genomic region as a result of the high degree of sequence homology between CYP21A2 and its pseudogene CYP21A1. Approximately 70% of CYP21A2 disease is due to gene conversion and micro-deletions in CYP21A1 gene.
Pathophysiology
- In patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency, there is a defective conversion of 17-hydroxyprogesterone to 11-deoxycortisol which results in decreased cortisol synthesis and therefore increased corticotropin (ACTH) secretion.
- The resulting adrenal stimulation leads to increased production of androgens.
- More than 95% of all cases of CAH are caused by 21-hydroxylase deficiency; the clinical manifestation of 21-hydroxylase deficiency is closely related to the type and severity of disease.
- The severity of disease relates to the mutation type which is caused enzyme inactivity or hypo activity.
- There is a lack of enzyme in classic type of 21-hydroxylase deficiency; while in the non-classic form, enzymatic activity is reduced but sufficient to maintain normal glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid production.
- Below is the hormonal pathway of adrenal steroids and related enzymes.[1][2]
Genetics
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia subtypes are all autosomal recessive and monogenetic. The disease manifestation follows the allele that results in a more functional enzyme, and generally correlation between genotype and phenotype is good.[3][4][3]
- Responsible gene for 21-hydroxylase deficiency is CYP21A. This gene is located within the human leucocyte antigen class III region of chromosome 6. CYP21A gene has two types:
- An active gene called CYP21A2, which encodes 21-hydroxylase, a cytochrome P450 type II enzyme of 495 amino acids.
- The other gene is a non-functional pseudogene named CYP21A1 or CYP21P. This pseudogene produces an enzyme with no activity because it lacks eight bases from codons 110-112, which results in a stop codon.[5]
- Meiotic recombination events occurs in this genomic region as a result of the high degree of sequence homology between CYP21A2 and its pseudogene CYP21A1.
- Approximately 70% of CYP21A2 disease is due to gene conversion and microdeletions in CYP21A1 gene.
- Approximately 25% to 30% are chimeric genes due to large deletions.
- Approximately 1% to 2% of cases are due to de novo mutations because of high variability of the CYP21A2 locus.
- Chromosome 6 uniparental disomy is rare cause of 21-hydroxylase deficiency with an unknown prevalence.
- Gene mutations that completely inactivate CYP21A2 gene will result in the classic type and salt-wasting subtype.
- Gene mutations that maintain 1–2% of 21-hydroxylase activity will result in classic type and non-salt-wasting subtype. These patients have minimal aldosterone production that prevents a neonatal adrenal crisis.[6]
Gross Pathology
Gross pathology findings in patients with 21 hydroxylase deficiency are:[7][8]
- Enlarged adrenal glands
- Wrinkled surface adrenal glands
- Cerebriform pattern adrenal glands (pathognomonic sign)
- Normal ultrasound appearances may also be seen
- Testicular masses may be identified representing adrenal rest tissue
Microscopic Pathology
In 21 hydroxylase deficiency microscopic findings may include:
- Diffuse cortical hyperplasia with smaller cells
- The cell cytoplasm can be vacuolated, and often more basophilic.
- Rare mitotic figures may be present
- The hyperplastic cells typically lack features of cellular atypia.[9]
 |
 |
References
- ↑ White PC, Speiser PW (2000). "Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency". Endocr. Rev. 21 (3): 245–91. doi:10.1210/edrv.21.3.0398. PMID 10857554.
- ↑ Speiser PW, Azziz R, Baskin LS, Ghizzoni L, Hensle TW, Merke DP, Meyer-Bahlburg HF, Miller WL, Montori VM, Oberfield SE, Ritzen M, White PC (2010). "Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95 (9): 4133–60. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2631. PMC 2936060. PMID 20823466.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Finkielstain GP, Chen W, Mehta SP, Fujimura FK, Hanna RM, Van Ryzin C, McDonnell NB, Merke DP (2011). "Comprehensive genetic analysis of 182 unrelated families with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96 (1): E161–72. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-0319. PMC 3038490. PMID 20926536.
- ↑ New MI, Abraham M, Gonzalez B, Dumic M, Razzaghy-Azar M, Chitayat D, Sun L, Zaidi M, Wilson RC, Yuen T (2013). "Genotype-phenotype correlation in 1,507 families with congenital adrenal hyperplasia owing to 21-hydroxylase deficiency". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110 (7): 2611–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.1300057110. PMC 3574953. PMID 23359698.
- ↑ White PC, New MI, Dupont B (1986). "Structure of human steroid 21-hydroxylase genes". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83 (14): 5111–5. PMC 323900. PMID 3487786.
- ↑ Fiet J, Gueux B, Gourmelen M, Kuttenn F, Vexiau P, Couillin P, Pham-Huu-Trung MT, Villette JM, Raux-Demay MC, Galons H (1988). "Comparison of basal and adrenocorticotropin-stimulated plasma 21-deoxycortisol and 17-hydroxyprogesterone values as biological markers of late-onset adrenal hyperplasia". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 66 (4): 659–67. doi:10.1210/jcem-66-4-659. PMID 2831244.
- ↑ Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Dr Henry Knipe and Dr M Venkatesh . Radiopaedia.org 2015.http://radiopaedia.org/articles/congenital-adrenal-hyperplasia
- ↑ Teixeira SR, Elias PC, Andrade MT, Melo AF, Elias Junior J (2014). "The role of imaging in congenital adrenal hyperplasia". Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 58 (7): 701–8. PMID 25372578.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 "Adrenal Gland - Hyperplasia - Nonneoplastic Lesion Atlas".