Sandbox:Sahar
Images

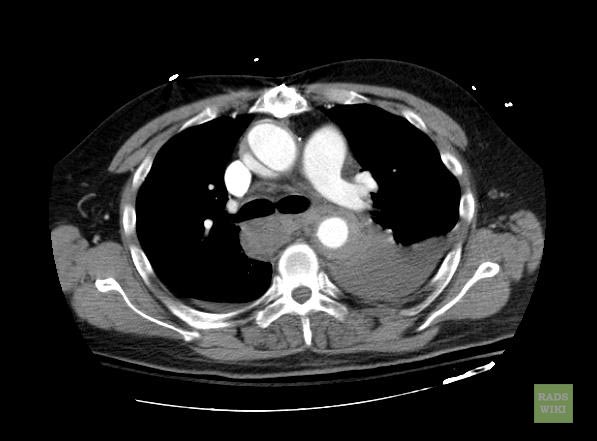
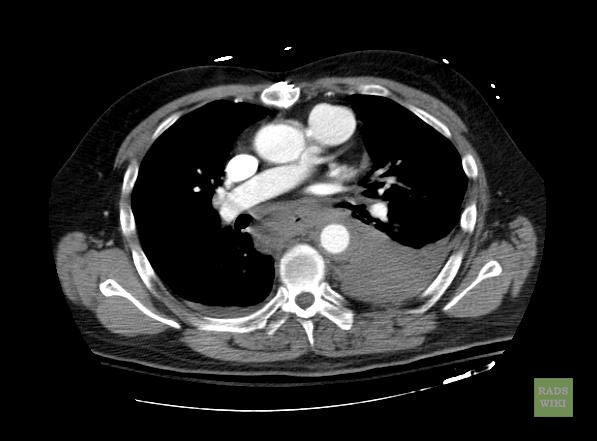
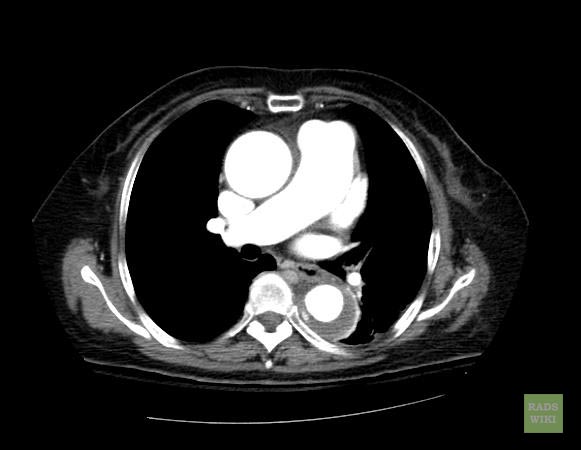
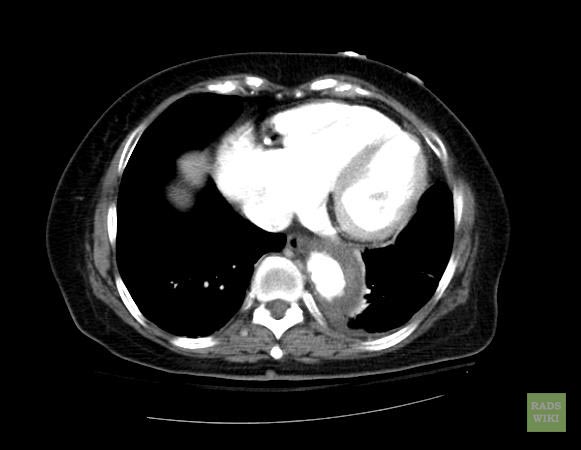
- Macura, Katarzyna J., Corl, Frank M., Fishman, Elliot K., Bluemke, David A. Pathogenesis in Acute Aortic Syndromes: Aortic Dissection, Intramural Hematoma, and Penetrating Atherosclerotic Aortic Ulcer. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003 181: 309-316.
- Gomez-Jorge, Jackeline. E-medicine rads article
| Disease Name | Causes | ECG Characteristics | ECG view |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ventricular tachycardia[1][2][3][4] |
|
| |
| Ventricular fibrillation |
|
|
|
| Asystole[5][6] |
|
 | |
| Pulseless electrical activity[7][8] |
|
|
 |
| Pulmonary embolism |
|
|
|
- ↑ Ajijola, Olujimi A.; Tung, Roderick; Shivkumar, Kalyanam (2014). "Ventricular tachycardia in ischemic heart disease substrates". Indian Heart Journal. 66: S24–S34. doi:10.1016/j.ihj.2013.12.039. ISSN 0019-4832.
- ↑ Meja Lopez, Eliany; Malhotra, Rohit (2019). "Ventricular Tachycardia in Structural Heart Disease". Journal of Innovations in Cardiac Rhythm Management. 10 (8): 3762–3773. doi:10.19102/icrm.2019.100801. ISSN 2156-3977.
- ↑ Coughtrie, Abigail L; Behr, Elijah R; Layton, Deborah; Marshall, Vanessa; Camm, A John; Shakir, Saad A W (2017). "Drugs and life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia risk: results from the DARE study cohort". BMJ Open. 7 (10): e016627. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016627. ISSN 2044-6055.
- ↑ El-Sherif, Nabil (2001). "Mechanism of Ventricular Arrhythmias in the Long QT Syndrome: On Hermeneutics". Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology. 12 (8): 973–976. doi:10.1046/j.1540-8167.2001.00973.x. ISSN 1045-3873.
- ↑ ACLS: Principles and Practice. p. 71-87. Dallas: American Heart Association, 2003. ISBN 0-87493-341-2.
- ↑ ACLS for Experienced Providers. p. 3-5. Dallas: American Heart Association, 2003. ISBN 0-87493-424-9.
- ↑ "2005 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care - Part 7.2: Management of Cardiac Arrest." Circulation 2005; 112: IV-58 - IV-66.
- ↑ Foster B, Twelve Lead Electrocardiography, 2nd edition, 2007
| Disease Name | Age of Onset | Gender Preponderance | Signs/Symptoms | Imaging Feature(s) | Macroscopic Feature(s) | Microscopic Feature(s) | Laboratory Findings(s) | Other Feature(s) | ECG view |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|