11β-hydroxylase deficiency pathophysiology
|
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
11β-hydroxylase deficiency pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of 11β-hydroxylase deficiency pathophysiology |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for 11β-hydroxylase deficiency pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ammu Susheela, M.D. [2]
Overview
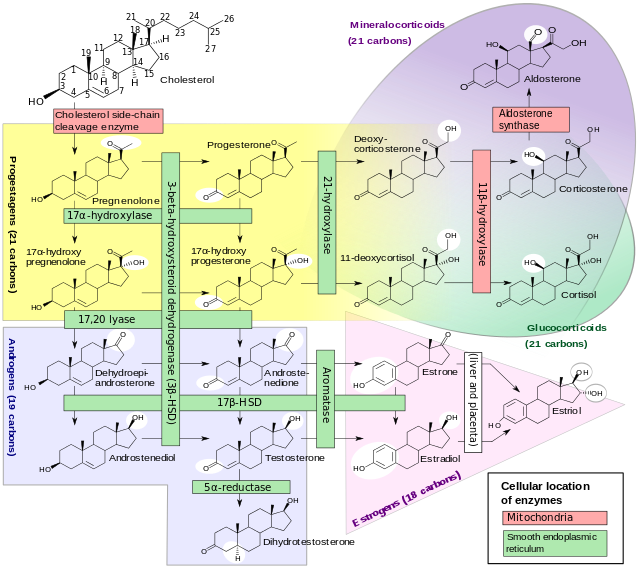
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency arises due to a defect in the gene encoding the enzyme steroid 11β-hydroxylase which mediates the final step of cortisol synthesis in the adrenal glands. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency is transmitted in an autosomal recessive pattern. On gross pathology, thickening of the adrenal gland and cerebriform appearance are characteristic findings of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency. On microscopic histopathological analysis, diffuse cortical hyperplasia and lipid-depleted cortical cells are characteristic findings of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency.
Pathogenesis
- 11β-Hydroxylase deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia (11β-OH CAH) is the second most common form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) resulting from a defect in the gene encoding the enzyme steroid 11β-hydroxylase which mediates the final step of cortisol synthesis in the adrenal. 11β-Hydroxylase deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia results in hypertension due to excessive mineralocorticoid effects. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency also causes excessive androgen production both before and after birth and can virilize a genetically female fetus or a child of either sex.
- When 11-beta-hydroxylase is lacking, precursors that are used to form cortisol and corticosterone build up in the adrenal glands and are converted to androgens. The excess production of androgens leads to abnormalities of sexual development, particularly in females with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency. A buildup in the precursors used to form corticosterone increases salt retention, leading to hypertension in individuals with the classic form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency.
Mineralocorticoid Effects
- Mineralocorticoid manifestations of severe congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency can be biphasic, changing from deficiency (salt-wasting) in early infancy to excess (hypertension) in childhood and adult life.
- The amount of functional 11-beta-hydroxylase enzyme that an individual produces typically determines the extent of abnormal sexual development.
- Salt-wasting in early infancy does not occur in most cases of 11β-hydroxylase deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia but can occur because of impaired production of aldosterone aggravated by the inefficiency of salt conservation in early infancy. Clinical features include poor weight gain and vomiting in the first weeks of life progress and culminate in life-threatening dehydration, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and metabolic acidosis in the first month.
- Despite the inefficient production of aldosterone, the more characteristic mineralocorticoid effect of 11β-hydroxylase deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia is hypertension. Progressive adrenal hyperplasia due to persistent elevation of adrenocorticotropic hormone results in extreme overproduction of 11-deoxycorticosterone (DOC) by mid-childhood. 11-Deoxycorticosterone is a weak mineralocorticoid, but usually reaches high enough levels in this disease to cause effects of mineralocorticoid excess: salt retention, volume expansion, and hypertension.[1]
Sex steroid Effects
- Because 11β-hydroxylase activity is not necessary in the production of sex steroids (androgens and estrogens), the hyperplastic adrenal cortex produces excessive amounts of dehydroepiandrosterone, androstenedione, and especially testosterone.
- These androgens produce effects that are similar to those of 21-hydroxylase deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia. In the severe forms, XX (genetically female) fetuses can be markedly virilized, with ambiguous genitalia that look more male than female, though internal female organs, including ovaries and uterus develop normally.
- XY fetuses (genetic males) typically show no abnormal features related to androgen excess. A megalopenis (>22 cm/8.7in) is usually present in male patients.
- In milder mutations, androgen effects in both sexes appear in mid-childhood as early pubic hair, overgrowth, and accelerated bone age. Although "nonclassic" forms causing hirsutism and menstrual irregularities and appropriate steroid elevations have been reported, most have not had verifiable mutations and mild 11β-hydroxylase deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia is currently considered a very rare cause of hirsutism and infertility.
- The enzyme which mediates 11β-hydroxylase activity is now known as P450c11β since it is one of the cytochrome P450 oxidase enzymes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane of cells of the adrenal cortex. It is coded by a gene at 8q21-22. Like the other forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, a number of different defective alleles for the gene have been identified, producing varying degrees of impaired 11β-hydroxylase activity. Also like the other forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, 11β-OH congenital adrenal hyperplasia is inherited as an autosomal recessive disease.
- 11β-Hydroxylase mediates the final step of the glucocorticoid pathway, producing cortisol from 11-deoxycortisol. It also catalyzes the conversion of 11-deoxycorticosterone (DOC) to corticosterone in the mineralocorticoid pathway.
- Females with the classic form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency have external genitalia that does not look clearly male or female (ambiguous genitalia). However, the internal reproductive organs develop normally. Males and females with the classic form of this condition have early development of their secondary sexual characteristics such as the growth of facial and pubic hair, deepening of the voice, the appearance of acne, and the onset of a growth spurt. The early growth spurt can prevent growth later in adolescence and lead to short stature in adulthood. In addition, approximately two-thirds of individuals with the classic form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency have hypertension. Hypertension typically develops within the first year of life.
- Females with the non-classic form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency have normal female genitalia. As affected females get older, they may develop excessive body hair growth (hirsutism) and irregular menstruation. Males with the non-classic form of this condition do not typically have any signs or symptoms except for short stature. Hypertension is not a feature of the non-classic form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency.[2]
Genetics
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition.
- Mutations in the CYP11B1 gene cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency. The CYP11B1 gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called 11-beta-hydroxylase. This enzyme is found in the adrenal glands, where it helps produce hormones called cortisol and corticosterone. Cortisol has numerous functions, such as maintaining blood sugar levels, protecting the body from stress, and suppressing inflammation. Corticosterone gets converted to the hormone aldosterone, which helps control blood pressure by maintaining proper salt and fluid levels in the body.
- Individuals with the classic form of the condition usually have CYP11B1 gene mutations that result in the production of an enzyme with low levels of function or no function at all. Individuals with the non-classic form of the condition typically have CYP11B1 gene mutations that lead to the production of an enzyme with moderately reduced function. The severity of the signs and symptoms of sexual development do not appear to be related to the severity of hypertension.

Associated Conditions
Gross Pathology
- On gross pathology the following changes are noted:
- Thickening of adrenal gland[3]
- Cerebriform appearance
Microscopic Pathology
- On microscopic pathology the following changes are noted:
- Diffuse cortical hyperplasia
- Zona reticularis is markedly hyperplastic
- Lipid depleted cortical cells
References
- ↑ Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency. Wikipedia (2016). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Congenital_adrenal_hyperplasia_due_to_11%CE%B2-hydroxylase_deficiency Accessed on January 29, 2016
- ↑ Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency. Genetic Home Reference (2016). http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/congenital-adrenal-hyperplasia-due-to-11-beta-hydroxylase-deficiency Accessed on January 25, 2016
- ↑ Adrenocortical hyperplasia. American urological association (2016). https://www.auanet.org/education/modules/pathology/adrenal-gland/hyperplasia.cfm Accessed on January 28, 2016