Iopromide
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
NOT FOR INTRATHECAL USE:
|
Overview
Iopromide is a radiographic contrast agent that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of cerebral arteriography and peripheral arteriography (300 mg i/ml), coronary arteriography and left ventriculography, visceral angiography and aortography (370 mg i/ml), peripheral venography (240 mg i/ml), contrast computed tomography (CT) imaging of head and body (300 mg i/ml and 370 mg i/ml), and excretory urography (300 mg i/ml). There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include headache, dysguesia, abnormal vision, chest pain, vasodilatation, nausea, vomiting, back pain, urinary urgency, injection site and infusion site reactions, and pain.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Intra-Arterial Procedures
- The volume and rate of injection of the contrast agent will vary depending on the injection site and the area being examined. Inject contrast at rates approximately equal to the flow rate in the vessel being injected.
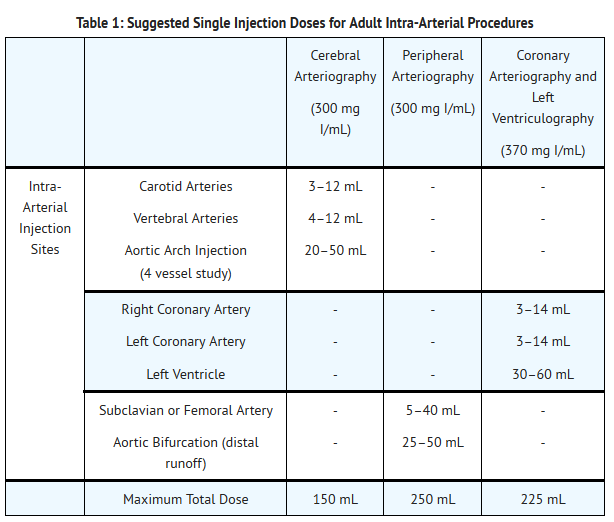
- Cerebral Arteriography (300 mg I/mL), Coronary Arteriography and Left Ventriculography (370 mg I/mL), Peripheral Arteriography (300 mg I/mL): see Table 1.
- Aortography and Visceral Angiography (370 mg I/mL):
- Use a volume and rate of contrast injection proportional to the blood flow and related to the vascular and pathological characteristics of the specific vessels being studied. Do not exceed 225 mL as total dose for the procedure.
T1
Intravenous Procedures
- Peripheral Venography (240 mg I/mL):
- Inject the minimum volume necessary to visualize satisfactorily the structures under examination. Do not exceed 250 mL as total dose for the procedure.
- Contrast Computed Tomography (CT) (300 mg I/mL and 370 mg I/mL) and Excretory Urography (300 mg I/mL): see Table 2.
T2
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Iopromide in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Iopromide in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- The recommended dose in children over 2 years of age for the following evaluations is:
Intra-arterial
- Cardiac chambers and related arteries (370 mg I/mL):
- Inject 1 to 2 milliliters per kilogram (mL/kg). Do not exceed 4 mL/kg as total dose.
Intravenous
- Contrast Computerized Tomography or Excretory Urography (300 mg I/mL):
- Inject 1 to 2 mL/kg. Do not exceed 3 mL/kg as total dose.
- The safety and efficacy relationships of other doses, concentrations or procedures have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Iopromide in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Iopromide in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Do not administer ULTRAVIST Injection intrathecally. Inadvertent intrathecal administration may cause death, convulsions, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, seizures, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema.
- Preparatory dehydration (for example, prolonged fasting and the administration of a laxative) before ULTRAVIST Injection is contraindicated in pediatric patients because of risk of acute renal failure.
Warnings
|
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
NOT FOR INTRATHECAL USE:
|
Precautions
- Anaphylactoid Reactions
- Life-threatening or fatal, anaphylactoid reactions, may occur during or after ULTRAVIST administration. Manifestations include respiratory arrest, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, angioedema, and shock. Increased risk is associated with a history of previous reaction to a contrast agent (3-fold), a known sensitivity to iodine and known allergic disorders (that is, bronchial asthma, hay fever and food allergies) or other hypersensitivities (2-fold) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Exercise extreme caution when considering the use of iodinated contrast agents in patients with these histories or disorders.
- Emergency facilities and personnel trained in the treatment of anaphylactoid reactions should be available for at least 30 to 60 minutes after ULTRAVIST administration.
- Acute Renal Failure
- Acute renal insufficiency or failure may occur following ULTRAVIST administration, particularly in patients with advanced vascular disease, congestive heart disease, diabetes, multiple myeloma or other paraproteinacious diseases, patients on medications which alter renal function and the elderly with age-related renal impairment. ULTRAVIST is cleared by glomerular filtration; patients with renal insufficiency have increased systemic exposure to ULTRAVIST as compared to patients with normal renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
- Exercise caution and use the lowest necessary dose of ULTRAVIST in patients with renal insufficiency. Adequately hydrate patients prior to and following ULTRAVIST administration. Patients with congestive heart failure receiving concurrent diuretic therapy may have relative intravascular volume depletion, which may affect the renal response to the contrast agent osmotic load. Observe such patients for several hours following the procedure to detect delayed hemodynamic renal function disturbances.
- Cardiovascular Reactions
- The increase in the circulatory osmotic load may induce acute or delayed hemodynamic disturbances in patients with congestive heart failure, severely impaired renal function, combined renal and hepatic disease, combined renal and cardiac disease, particularly when repetitive and/or large doses are administered [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- Among patients who have had cardiovascular reactions, most deaths occurred from the start of injection to 10 minutes later; the main feature was cardiac arrest with cardiovascular disease as the main underlying factor. Isolated reports of hypotensive collapse and shock have been published. Based upon published reports, deaths from the administration of iodinated contrast agents range from 6.6 per 1 million (0.00066 percent) to 1 in 10,000 patients (0.01 percent). Observe patients with preexisting cardiovascular disease for several hours following ULTRAVIST administration.
- Thromboembolic Complications
- Angiography may be associated with local and distal organ damage, ischemia, thromboembolism and organ failure including stroke, brachial plexus palsy, chest pain, myocardial infarction, sinus arrest, hepato-renal function abnormalities. For these reasons, meticulous angiographic techniques are recommended, including close attention to guide wire and catheter manipulation, use of manifold systems and/or three-way stopcocks, frequent catheter flushing with heparinized saline solutions and minimizing the length of the procedure. In angiographic procedures, consider the possibility of dislodging plaques or damaging or perforating the vessel wall with resultant pseudoaneurysms, hemorrhage at puncture site, dissection of coronary artery during catheter manipulations and contrast agent injection. The physicochemical properties of the contrast agent, the dose and the speed of injection can influence the reactions. Test injections to ensure proper catheter placement are suggested. Increased thrombosis and activation of the complement system has also occurred. Specialized personnel, and adequate equipment and facilities for immediate resuscitation and cardioversion are necessary. Monitor electrocardiograms and vital signs throughout the procedure.
- Clotting may occur when blood remains in contact with syringes containing iodinated contrast agents.
- Avoid angiography whenever possible in patients with homocystinuria because of the risk of inducing thrombosis and embolism [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
- Reactions in Patients with Hyperthyroidism, Pheochromocytoma, or Sickle Cell Disease
- Thyroid storm in patients with hyperthyroidism. Thyroid storm has occurred after the intravascular use of iodinated contrast agents in patients with hyperthyroidism, or with an autonomously functioning thyroid nodule. Evaluate the risk in such patients before use of any iodinated contrast agent.
- Hypertensive crises in patients with pheochromocytoma. Administer iodinated contrast agents with extreme caution in patients with known or suspected of having pheochromocytoma. Inject the minimum amount of contrast necessary. Assess the blood pressure throughout the procedure, and have measures for treatment of a hypertensive crisis readily available.
- Sickle cell disease. Contrast agents may promote sickling in individuals who are homozygous for sickle cell disease when administered intravascularly.
- Extravasation
- Extravasation of ULTRAVIST Injection may cause tissue necrosis and/or compartment syndrome, particularly in patients with severe arterial or venous disease.
- Increased Radiation Exposure
- The decision to use contrast enhancement is associated with risk and increased radiation exposure. Use contrast after a careful evaluation of clinical, other radiologic data, and the results of non-contrast CT findings, taking into account the increased radiation dose and other risks.
- Interference with Image Interpretation
- As with other iodinated contrast agents, the use of ULTRAVIST Injection may obscure some lesions which were seen on non-contrast CT scans.
- Calcified lesions are less likely to enhance. The enhancement of tumors after therapy may decrease. The opacification of the inferior vermis following contrast agent administration has resulted in false-positive diagnosis. Cerebral infarctions of recent onset may be better visualized with contrast enhancement. However, older infarctions may be obscured by the contrast agent.
- In patients with normal blood-brain barriers and renal failure, iodinated contrast agents have been associated with blood-brain barrier disruption and accumulation of contrast in the brain. Accumulation of contrast in the brain also occurs in patients where the blood-brain barrier is known or suspected to be disrupted.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect or predict the rates observed in practice.
- The following table of incidence of reactions is based upon controlled clinical trials in which ULTRAVIST Injection was administered to 1142 patients. This listing includes all reported adverse reactions regardless of attribution.
- Adverse reactions are listed by System Organ Class and in decreasing order of occurrence for rates greater than 1% in the ULTRAVIST group.
T3
- One or more adverse reactions were recorded in 273 of 1142 (24%) patients during the clinical trials, coincident with the administration of ULTRAVIST Injection or within the defined duration of the study follow-up period (24–72 hours). ULTRAVIST Injection is often associated with sensations of warmth and/or pain.
- Serious, life-threatening and fatal reactions have been associated with the administration of iodine-containing contrast media, including ULTRAVIST Injection. In clinical trials 7/1142 patients given ULTRAVIST Injection died 5 days or later after drug administration. Also, 10/1142 patients given ULTRAVIST Injection had serious adverse events.
- The following adverse reactions were observed in ≤1% of the subjects receiving ULTRAVIST Injection:
Cardiac disorders
Atrio ventricular block (complete), bradycardia, ventricular extrasystole;
Gastrointestinal disorders
Abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, gastrointestinal disorder, gastrointestinal pain, salivation increased, stomach discomfort, rectal tenesmus;
General disorders and administration site conditions
Asthenia, chest discomfort, chills, excessive thirst, extravasation, feeling hot, hyperhydrosis, malaise, edema peripheral, pyrexia;
Immune system disorders
Asthma, face edema;
Investigations
Blood lactate dehydrogenase increased, blood urea increased, hemoglobin increased, white blood cell count increased;
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Arthralgia, musculoskeletal pain, myasthenia, neck pain, pain in extremity;
Nervous system disorders
Agitation, confusion, convulsion, dizziness, hypertonia, hypesthesia, incoordination, neuropathy, somnolence, speech disorder, tremor, paresthesia, visual field defect;
Psychiatric disorders
Anxiety;
Renal and urinary disorders
Dysuria, renal pain, urinary retention;
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Apnea, cough increased, dyspnea, hypoxia, pharyngeal edema, pharyngitis, pleural effusion, pulmonary hypertension, respiratory disorder, sore throat;
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Erythema, pruritus, rash, urticaria;
Vascular disorders
Coronary artery thrombosis, flushing, hypertension, hypotension, peripheral vascular disorder, syncope, vascular anomaly.
Pediatrics
- The overall character, quality, and severity of adverse reactions in pediatric patients are generally similar to those reported in adult patients. Additional adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients from foreign marketing surveillance or other information are: epistaxis, angioedema, migraine, joint disorder (effusion), muscle cramps, mucous membrane disorder (mucosal swelling), conjunctivitis, hypoxia, fixed eruptions, vertigo, diabetes insipidus, and brain edema.
Postmarketing Experience
- The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of ULTRAVIST Injection. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Adverse reactions reported in foreign postmarketing surveillance and other trials with the use of ULTRAVIST Injection include:
Cardiac disorders
Cardiac arrest, ventricular fibrillation, atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, palpitations, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris;
Ear and labyrinth disorders
Vertigo, tinnitus;
Endocrine disorders
Hyperthyroidism, thyrotoxic crisis, hypothyroidism;
Eye disorders
Mydriasis, lacrimation disorder;
Gastrointestinal disorders
Dysphagia, swelling of salivary glands;
Immune system disorders
Anaphylactoid reaction (including fatal cases), respiratory arrest, anaphylactoid shock, angioedema, laryngeal edema, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, hypersensitivity;
Nervous system disorders
Cerebral ischemia/infarction, paralysis, paresis, transient cortical blindness, aphasia, coma, unconsciousness, amnesia, hypotonia;
Renal and urinary disorders
Renal failure, hematuria;
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome, asthma;
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, skin discoloration;
Vascular disorders
Vasospasm.
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Iopromide in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Iopromide during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Iopromide with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Iopromide with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Iopromide with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Iopromide with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Iopromide with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Iopromide in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Iopromide in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Iopromide in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Iopromide in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Iopromide in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Iopromide in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Iopromide in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Iopromide Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Iopromide in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Iopromide in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Iopromide in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Iopromide in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Iopromide Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Iopromide |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Iopromide |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Iopromide in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Iopromide interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Iopromide |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Iopromide |Label Name=Iopromide11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Iopromide |Label Name=Iopromide11.png
}}