DIGOXIN injection description: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "__NOTOC__ {{Digoxin}} {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{AK}} '''''For patient information, click <u>here'''''</u>. ==11 DESCRIPTION== Digoxin is one of th...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
'''''For patient information, click <u>[[Digoxin (patient information)|here]]'''''</u>. | '''''For patient information, click <u>[[Digoxin (patient information)|here]]'''''</u>. | ||
== | == Description== | ||
Digoxin is one of the cardiac (or [[digitalis]]) [[glycosides]], a closely related group of drugs having in common specific effects on the myocardium. These drugs are found in a number of plants. Digoxin is extracted from the leaves of Digitalis lanata. The term “digitalis” is used to designate the whole group of glycosides. The glycosides are composed of 2 portions: a sugar and a cardenolide (hence “glycosides”). | Digoxin is one of the cardiac (or [[digitalis]]) [[glycosides]], a closely related group of drugs having in common specific effects on the myocardium. These drugs are found in a number of plants. Digoxin is extracted from the leaves of Digitalis lanata. The term “digitalis” is used to designate the whole group of glycosides. The glycosides are composed of 2 portions: a sugar and a cardenolide (hence “glycosides”). | ||
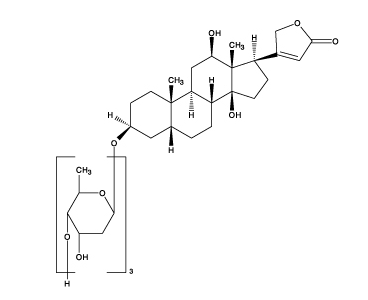
Digoxin is described chemically as (3β,5β,12β)-3-[(O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-12,14-dihydroxy-card-20(22)-enolide. Its molecular formula is C41H64O14, its molecular weight is 780.95, and its structural formula is: | Digoxin is described chemically as (3β,5β,12β)-3-[(O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-12,14-dihydroxy-card-20(22)-enolide. Its molecular formula is C41H64O14, its molecular weight is 780.95, and its structural formula is: | ||
{| | |||
[[image:diginj9.png]] | |[[image:diginj9.png|600px|thumb]] | ||
|} | |||
Digoxin exists as clear to white odorless crystals or white, odorless crystalline powder that melts with decomposition above 230°C. The drug is practically insoluble in water and in ether; slightly soluble in diluted (50%) alcohol and in chloroform; and freely soluble in pyridine. | Digoxin exists as clear to white odorless crystals or white, odorless crystalline powder that melts with decomposition above 230°C. The drug is practically insoluble in water and in ether; slightly soluble in diluted (50%) alcohol and in chloroform; and freely soluble in pyridine. | ||
Revision as of 04:26, 13 March 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Abdurahman Khalil, M.D. [2]
For patient information, click here.
Description
Digoxin is one of the cardiac (or digitalis) glycosides, a closely related group of drugs having in common specific effects on the myocardium. These drugs are found in a number of plants. Digoxin is extracted from the leaves of Digitalis lanata. The term “digitalis” is used to designate the whole group of glycosides. The glycosides are composed of 2 portions: a sugar and a cardenolide (hence “glycosides”).
Digoxin is described chemically as (3β,5β,12β)-3-[(O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-12,14-dihydroxy-card-20(22)-enolide. Its molecular formula is C41H64O14, its molecular weight is 780.95, and its structural formula is:
 |
Digoxin exists as clear to white odorless crystals or white, odorless crystalline powder that melts with decomposition above 230°C. The drug is practically insoluble in water and in ether; slightly soluble in diluted (50%) alcohol and in chloroform; and freely soluble in pyridine.
Digoxin injection USP is a sterile solution of digoxin for intravenous or intramuscular injection. Each mL contains: digoxin 0.25 mg, propylene glycol 40% (v/v), anhydrous ethanol 10% (v/v), dibasic sodium phosphate 0.3% (w/v) and anhydrous citric acid 0.08% (w/v) to adjust pH between 6.8 and 7.2, and water for injection. Dilution is not required.
References
http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=58f45aba-ff6f-43cc-bb88-be40a9f7beda