WBR0387: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{WBRQuestion |QuestionAuthor={{Rim}} |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 |MainCategory=Physiology |SubCategory=Renal |MainCategory=Physiology |SubCategory=Renal |MainCategory=Physiology |...") |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|MainCategory=Physiology | |MainCategory=Physiology | ||
|SubCategory=Renal | |SubCategory=Renal | ||
|Prompt=A researcher is studying the role of aldosterone at the level of renal tubules. He conducts an experiment whereby he measures urinary concentration of sodium, potassium, and hydrogen before and after aldosterone administration. With respect to urinary concentrations before the administration of aldosterone, which of the following parameters is true for concentrations of urinary sodium, potassium, and hydrogen after aldosterone administration? | |Prompt=A researcher is studying the role of aldosterone at the level of renal tubules. He conducts an experiment whereby he measures urinary concentration of sodium, potassium, and hydrogen before and after aldosterone administration. With respect to urinary concentrations before the administration of aldosterone, which of the following parameters is true for concentrations of urinary sodium, potassium, and hydrogen (in order) after aldosterone administration? | ||
[[Image:Urinary Electrolytes Aldosteron WBR.png|450px]] | |||
|Explanation=Aldosterone accelerates the ion exchange of sodium for potassium or hydrogen. Aldosterone acts at the level of collecting ducts to reabsorb sodium, and excrete potassium and hydrogen. Thus, urinary concentrations of sodium will be decreased, while urinary concentrations of potassium and hydrogen will be increased. | |Explanation=Aldosterone accelerates the ion exchange of sodium for potassium or hydrogen. Aldosterone acts at the level of collecting ducts to reabsorb sodium, and excrete potassium and hydrogen. Thus, urinary concentrations of sodium will be decreased, while urinary concentrations of potassium and hydrogen will be increased. | ||
Educational Objective: | Educational Objective: | ||
Aldosterone acts on the renal collecting tubule. It accelerates the ion exchange of sodium for potassium or hydrogen; allowing increased reabsorption of sodium and excretion of both potassium and hydrogen. | Aldosterone acts on the renal collecting tubule. It accelerates the ion exchange of sodium for potassium or hydrogen; allowing increased reabsorption of sodium and excretion of both potassium and hydrogen. | ||
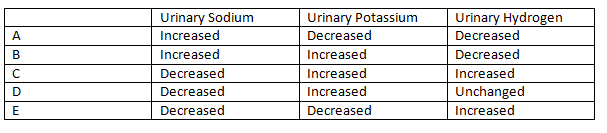
|AnswerA=Increased - Decreased - Decreased | |||
|AnswerA=Increased Decreased Decreased | |||
|AnswerAExp=An increase in sodium, accompanied by a decrease in potassium and hydrogen, is seen in the serum, not in urine. | |AnswerAExp=An increase in sodium, accompanied by a decrease in potassium and hydrogen, is seen in the serum, not in urine. | ||
|AnswerB=Increased Increased Decreased | |AnswerB=Increased - Increased - Decreased | ||
|AnswerBExp=Following aldosterone administration, urinary sodium is decreased due to aldsoterone’s activity in reabsorbing sodium, and urinary hydrogen is increased due to aldosterone’s activity in excreting hydrogen. | |AnswerBExp=Following aldosterone administration, urinary sodium is decreased due to aldsoterone’s activity in reabsorbing sodium, and urinary hydrogen is increased due to aldosterone’s activity in excreting hydrogen. | ||
|AnswerC=Decreased Increased Increased | |AnswerC=Decreased - Increased - Increased | ||
|AnswerCExp=Aldosterone accelerates the ion exchange of sodium for potassium or hydrogen; allowing increased reabsorption of sodium and excretion of both potassium and hydrogen. | |AnswerCExp=Aldosterone accelerates the ion exchange of sodium for potassium or hydrogen; allowing increased reabsorption of sodium and excretion of both potassium and hydrogen. | ||
|AnswerD=Decreased Increased Unchanged | |AnswerD=Decreased - Increased - Unchanged | ||
|AnswerDExp=Following aldosterone administration, hydrogen is excreted. Its urinary concentration will be increased. It will not remain unchanged. | |AnswerDExp=Following aldosterone administration, hydrogen is excreted. Its urinary concentration will be increased. It will not remain unchanged. | ||
|AnswerE=Decreased Decreased Increased | |AnswerE=Decreased - Decreased - Increased | ||
|AnswerEExp=Following aldosterone administration, urinary potassium increases, while serum potassium is decreased due to aldosterone’s activity in excreting potassium. | |AnswerEExp=Following aldosterone administration, urinary potassium increases, while serum potassium is decreased due to aldosterone’s activity in excreting potassium. | ||
|RightAnswer=C | |RightAnswer=C | ||
|Approved=No | |Approved=No | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 03:36, 10 September 2013
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1]]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Physiology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Renal |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A researcher is studying the role of aldosterone at the level of renal tubules. He conducts an experiment whereby he measures urinary concentration of sodium, potassium, and hydrogen before and after aldosterone administration. With respect to urinary concentrations before the administration of aldosterone, which of the following parameters is true for concentrations of urinary sodium, potassium, and hydrogen (in order) after aldosterone administration? |
| Answer A | [[AnswerA::Increased - Decreased - Decreased]] |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::An increase in sodium, accompanied by a decrease in potassium and hydrogen, is seen in the serum, not in urine. |
| Answer B | [[AnswerB::Increased - Increased - Decreased]] |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::Following aldosterone administration, urinary sodium is decreased due to aldsoterone’s activity in reabsorbing sodium, and urinary hydrogen is increased due to aldosterone’s activity in excreting hydrogen. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Decreased - Increased - Increased |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::Aldosterone accelerates the ion exchange of sodium for potassium or hydrogen; allowing increased reabsorption of sodium and excretion of both potassium and hydrogen. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Decreased - Increased - Unchanged |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::Following aldosterone administration, hydrogen is excreted. Its urinary concentration will be increased. It will not remain unchanged. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Decreased - Decreased - Increased |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::Following aldosterone administration, urinary potassium increases, while serum potassium is decreased due to aldosterone’s activity in excreting potassium. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::C |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Aldosterone accelerates the ion exchange of sodium for potassium or hydrogen. Aldosterone acts at the level of collecting ducts to reabsorb sodium, and excrete potassium and hydrogen. Thus, urinary concentrations of sodium will be decreased, while urinary concentrations of potassium and hydrogen will be increased.
Educational Objective:
Aldosterone acts on the renal collecting tubule. It accelerates the ion exchange of sodium for potassium or hydrogen; allowing increased reabsorption of sodium and excretion of both potassium and hydrogen. |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |