Sandbox:Sahar: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 182: | Line 182: | ||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[File:ThyroidnodularSatturwar08.jpg|thumb|none|200px|Source:pathology outline, case courtesy of Dr. Swati Satturwar]] | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[File:ThyroidnodularSatturwar08.jpg|thumb|none|200px|Source:pathology outline, case courtesy of Dr. Swati Satturwar]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; " align="left" |Thyroid Lymphoma | ! style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; " align="left" |Thyroid Lymphoma<ref name="pmid8838117">{{cite journal |vauthors=Pedersen RK, Pedersen NT |title=Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the thyroid gland: a population based study |journal=Histopathology |volume=28 |issue=1 |pages=25–32 |date=January 1996 |pmid=8838117 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
<ref name="pmid3141260">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hyjek E, Isaacson PG |title=Primary B cell lymphoma of the thyroid and its relationship to Hashimoto's thyroiditis |journal=Hum. Pathol. |volume=19 |issue=11 |pages=1315–26 |date=November 1988 |pmid=3141260 |doi=10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80287-9 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid3759532">{{cite journal |vauthors=Tupchong L, Hughes F, Harmer CL |title=Primary lymphoma of the thyroid: clinical features, prognostic factors, and results of treatment |journal=Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. |volume=12 |issue=10 |pages=1813–21 |date=October 1986 |pmid=3759532 |doi=10.1016/0360-3016(86)90324-x |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17042683">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ota H, Ito Y, Matsuzuka F, Kuma S, Fukata S, Morita S, Kobayashi K, Nakamura Y, Kakudo K, Amino N, Miyauchi A |title=Usefulness of ultrasonography for diagnosis of malignant lymphoma of the thyroid |journal=Thyroid |volume=16 |issue=10 |pages=983–7 |date=October 2006 |pmid=17042683 |doi=10.1089/thy.2006.16.983 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | ||
* Affects adults or elderly | * Affects adults or elderly | ||
| Line 209: | Line 209: | ||
* Some may have [[hypothyroidism]] | * Some may have [[hypothyroidism]] | ||
* Some may have [[antibody]] against [[thyroid peroxidase]] or [[thyroglobulin]] | * Some may have [[antibody]] against [[thyroid peroxidase]] or [[thyroglobulin]] | ||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | ||
* Preexisting chronic [[Hashimoto's thyroiditis|autoimmune (Hashimoto's) thyroiditis]] is a known [[risk factor]] for this [[condition]] | * Preexisting chronic [[Hashimoto's thyroiditis|autoimmune (Hashimoto's) thyroiditis]] is a known [[risk factor]] for this [[condition]] | ||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[File:Thyroid lymphoma large cell type fine needle aspiration biop.jpeg|thumb|none|200px|Source:pathology outline, case courtesy of Dr. Mark R. Wick]] | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[File:Thyroid lymphoma large cell type fine needle aspiration biop.jpeg|thumb|none|200px|Source:pathology outline, case courtesy of Dr. Mark R. Wick]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 18:03, 29 July 2019
| Disease name | Age of onset | Gender preponderance | Signs/Symptoms | Imaging Feature(s) | Macroscopic feature(s) | Microscopic feature(s) | Laboratory Feature(s) | Other Feature(s) | Microscopic appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Papillary Thyroid Cancer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
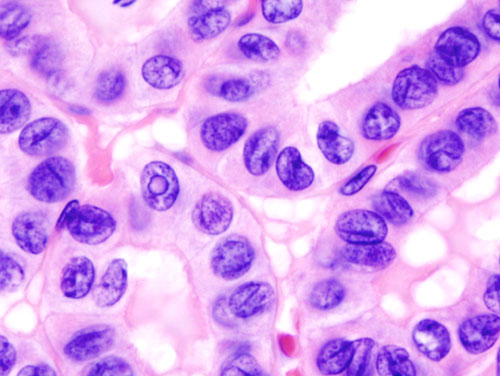 | |
| Follicular Thyroid Cancer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
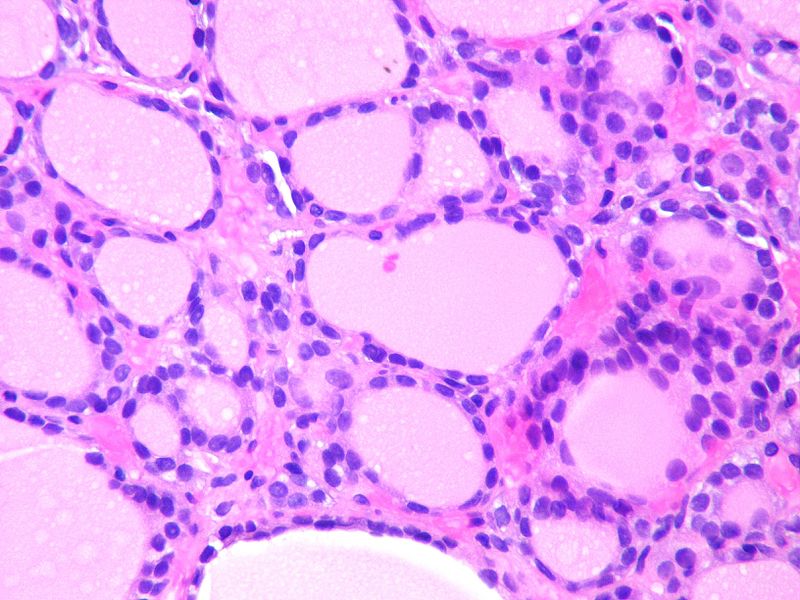 | |
| Medullary Thyroid Cancer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 | |
| Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
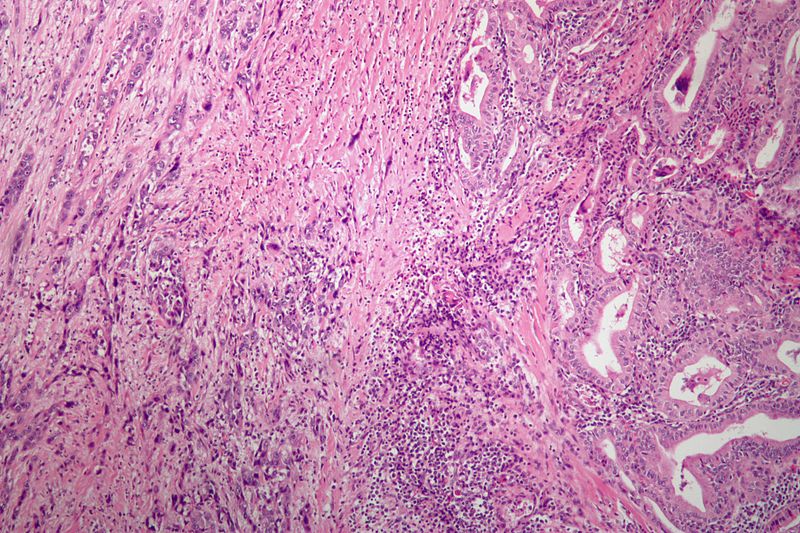 | ||
| Thyroid Adenoma |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 | ||
| Multinodular Goiter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
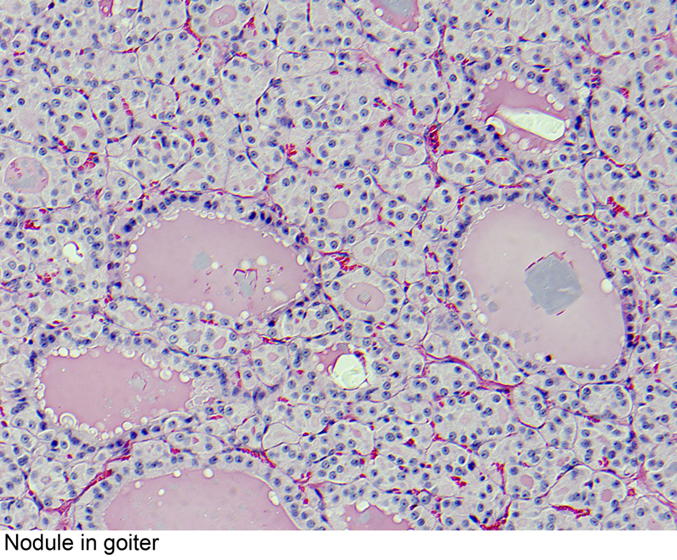 | |
| Thyroid Lymphoma[1] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
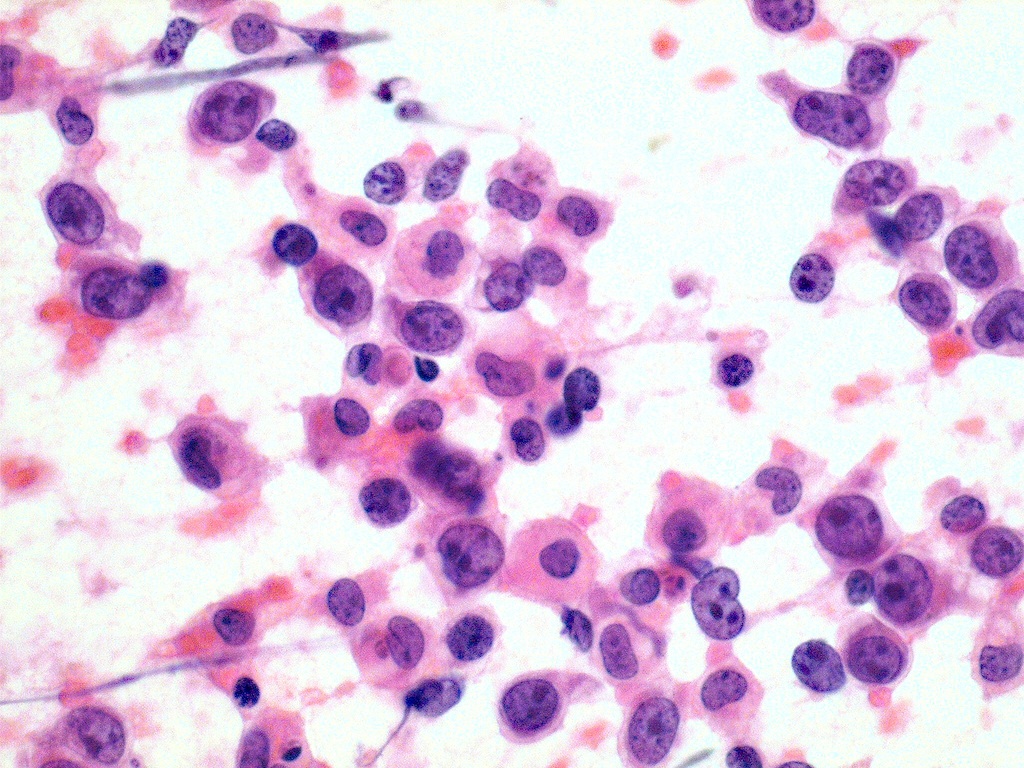 |
- ↑ Pedersen RK, Pedersen NT (January 1996). "Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the thyroid gland: a population based study". Histopathology. 28 (1): 25–32. PMID 8838117.
- ↑ Hyjek E, Isaacson PG (November 1988). "Primary B cell lymphoma of the thyroid and its relationship to Hashimoto's thyroiditis". Hum. Pathol. 19 (11): 1315–26. doi:10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80287-9. PMID 3141260.
- ↑ Tupchong L, Hughes F, Harmer CL (October 1986). "Primary lymphoma of the thyroid: clinical features, prognostic factors, and results of treatment". Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 12 (10): 1813–21. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(86)90324-x. PMID 3759532.
- ↑ Ota H, Ito Y, Matsuzuka F, Kuma S, Fukata S, Morita S, Kobayashi K, Nakamura Y, Kakudo K, Amino N, Miyauchi A (October 2006). "Usefulness of ultrasonography for diagnosis of malignant lymphoma of the thyroid". Thyroid. 16 (10): 983–7. doi:10.1089/thy.2006.16.983. PMID 17042683.