Trifluridine and tipiracil: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage |authorTag={{AKT}} |genericName=trifluridine and tipiracil |aOrAn=a |drugClass=combination of a nucleoside metabolic inhibitor and a ...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
|blackBoxWarningTitle='''<span style="color:#FF0000;"></span>''' | |blackBoxWarningTitle='''<span style="color:#FF0000;"></span>''' | ||
|blackBoxWarningBody=''<span style="color:#FF0000;"></span>'' | |blackBoxWarningBody=''<span style="color:#FF0000;"></span>'' | ||
|fdaLIADAdult=LONSURF is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who have been previously treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin- and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, an anti-VEGF biological therapy, and if RAS wild-type, an anti-EGFR therapy. | |||
'''Dosing Information''' | |||
*The recommended starting dose of LONSURF is 35 mg/m2 up to a maximum of 80 mg per dose (based on the trifluridine component) orally twice daily within one hour of completion of morning and evening meals on Days 1 through 5 and Days 8 through 12 of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. | |||
*Round dose to the nearest 5 mg increment. | |||
*Do not take additional doses to make up for missed or held doses. | |||
*Do not initiate the cycle of LONSURF until: | |||
**Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is greater than or equal to 1,500/mm3 or febrile neutropenia is resolved | |||
**Platelets are greater than or equal to 75,000/mm3 | |||
**Grade 3 or 4 non-hematological adverse reactions are resolved to Grade 0 or 1 | |||
*Within a treatment cycle, withhold LONSURF for any of the following: | |||
**Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) less than 500/mm3 or febrile neutropenia | |||
**Platelets less than 50,000/mm3 | |||
**Grade 3 or 4 non-hematological adverse reactions | |||
*After recovery, resume LONSURF after reducing the dose by 5 mg/m2/dose from the previous dose level, if the following occur: | |||
**Febrile neutropenia | |||
**Uncomplicated Grade 4 neutropenia (which has recovered to greater than or equal to 1,500/mm3) or thrombocytopenia (which has recovered to greater than or equal to 75,000/mm3) that results in more than 1 week delay in start of next cycle | |||
**Non-hematologic Grade 3 or Grade 4 adverse reaction except for Grade 3 nausea and/or vomiting controlled by antiemetic therapy or Grade 3 diarrhea responsive to antidiarrheal medication | |||
*A maximum of 3 dose reductions are permitted to a minimum dose of 20 mg/m2 twice daily. Do not escalate LONSURF dose after it has been reduced. | |||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding ''Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use'' of Trifluridine and tipiracil in adult patients. | |offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding ''Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use'' of Trifluridine and tipiracil in adult patients. | ||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding ''Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use'' of Trifluridine and tipiracil in adult patients. | |offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding ''Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use'' of Trifluridine and tipiracil in adult patients. | ||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding ''Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use'' of Trifluridine and tipiracil in pediatric patients. | |offLabelPedGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding ''Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use'' of Trifluridine and tipiracil in pediatric patients. | ||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding ''Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use'' of Trifluridine and tipiracil in pediatric patients. | |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding ''Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use'' of Trifluridine and tipiracil in pediatric patients. | ||
|warnings=*Severe Myelosuppression | |||
**In Study 1, LONSURF caused severe and life-threatening myelosuppression (Grade 3-4) consisting of anemia (18%), neutropenia (38%), thrombocytopenia (5%) and febrile neutropenia (3.8%). One patient (0.2%) died due to neutropenic infection. In Study 1, 9.4% of LONSURF-treated patients received granulocyte-colony stimulating factors. | |||
**Obtain complete blood counts prior to and on Day 15 of each cycle of LONSURF and more frequently as clinically indicated. Withhold LONSURF for febrile neutropenia, Grade 4 neutropenia, or platelets less than 50,000/mm3. Upon recovery resume LONSURF at a reduced dose. | |||
*Embryo-Fetal Toxicity | |||
**Based on animal studies and its mechanism of action, LONSURF can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Trifluridine/tipiracil caused embryo-fetal lethality and embryo-fetal toxicity in pregnant rats when orally administered during gestation at dose levels resulting in exposures lower than those achieved at the recommended dose of 35 mg/m2 twice daily. | |||
**Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LONSURF. | |||
|clinicalTrials=Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. | |||
The data described below are from Study 1, a randomized (2:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which 533 patients (median age 63 years; 61% men; 57% White, 35% Asian, 1% Black) with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer received LONSURF as a single agent at a dose of 35 mg/m2/dose administered twice daily on Days 1 through 5 and Days 8 through 12 of each 28-day cycle. The mean duration of LONSURF therapy was 12.7 weeks. | |||
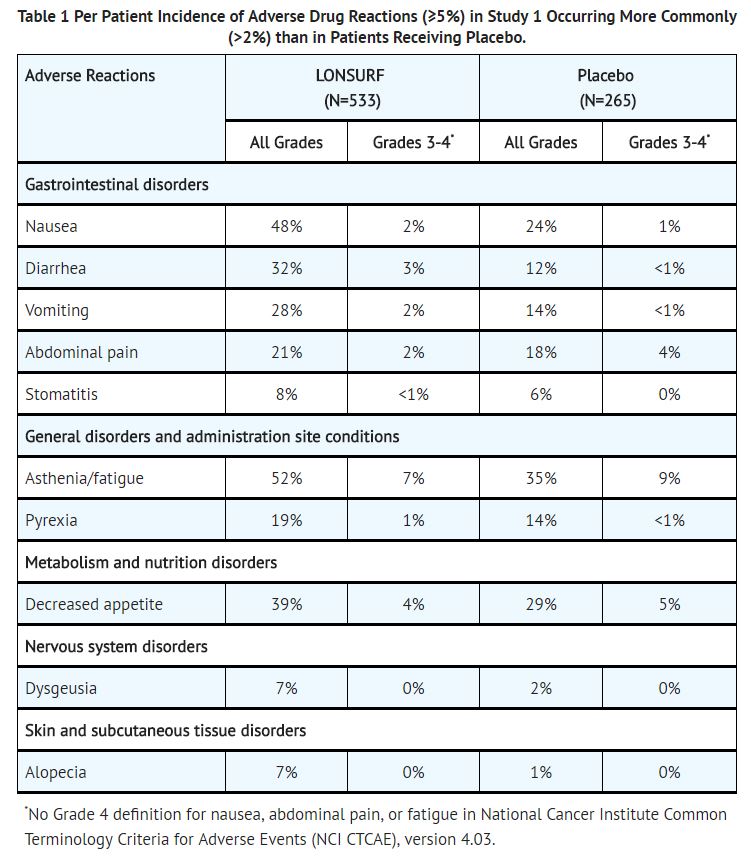
The most common adverse drug reactions or laboratory abnormalities (all Grades and greater than or equal to 10% in incidence) in patients treated with LONSURF at a rate that exceeds the rate in patients receiving placebo were anemia, neutropenia, asthenia/fatigue, nausea, thrombocytopenia, decreased appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and pyrexia. | |||
In Study 1, 3.6% of patients discontinued LONSURF for an adverse event and 13.7% of patients required a dose reduction. The most common adverse reactions leading to dose reduction were neutropenia, anemia, febrile neutropenia, fatigue, and diarrhea. | |||
[[File:Trifluridine and tipiracil T1.JPG|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine]] | |||
[[File:Trifluridine and tipiracil T2.JPG|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine]] | |||
In Study 1, infections occurred more frequently in LONSURF-treated patients (27%) compared to those receiving placebo (15%). The most commonly reported infections which occurred more frequently in LONSURF-treated patients were nasopharyngitis (4% versus 2%), and urinary tract infections (4% versus 2%). | |||
In Study 1, pulmonary emboli occurred more frequently in LONSURF-treated patients (2%) compared to no patients on placebo. | |||
Additional Clinical Experience: | |||
Interstitial lung disease was reported in fifteen (0.2%) patients, three of which were fatal, among approximately 7,000 patients exposed to LONSURF in clinical studies and clinical practice settings in Asia. | |||
|alcohol=Alcohol-Trifluridine and tipiracil interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |alcohol=Alcohol-Trifluridine and tipiracil interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 13:46, 26 July 2017
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Allison Tu [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Trifluridine and tipiracil is a combination of a nucleoside metabolic inhibitor and a thymidine phosphorylase inhibitor that is FDA approved for the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who have been previously treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin- and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, an anti-VEGF biological therapy, and if RAS wild-type, an anti-EGFR therapy. Common adverse reactions include fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, abdominal pain, anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, weakness, and fever.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
LONSURF is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who have been previously treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin- and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, an anti-VEGF biological therapy, and if RAS wild-type, an anti-EGFR therapy.
Dosing Information
- The recommended starting dose of LONSURF is 35 mg/m2 up to a maximum of 80 mg per dose (based on the trifluridine component) orally twice daily within one hour of completion of morning and evening meals on Days 1 through 5 and Days 8 through 12 of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
- Round dose to the nearest 5 mg increment.
- Do not take additional doses to make up for missed or held doses.
- Do not initiate the cycle of LONSURF until:
- Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is greater than or equal to 1,500/mm3 or febrile neutropenia is resolved
- Platelets are greater than or equal to 75,000/mm3
- Grade 3 or 4 non-hematological adverse reactions are resolved to Grade 0 or 1
- Within a treatment cycle, withhold LONSURF for any of the following:
- Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) less than 500/mm3 or febrile neutropenia
- Platelets less than 50,000/mm3
- Grade 3 or 4 non-hematological adverse reactions
- After recovery, resume LONSURF after reducing the dose by 5 mg/m2/dose from the previous dose level, if the following occur:
- Febrile neutropenia
- Uncomplicated Grade 4 neutropenia (which has recovered to greater than or equal to 1,500/mm3) or thrombocytopenia (which has recovered to greater than or equal to 75,000/mm3) that results in more than 1 week delay in start of next cycle
- Non-hematologic Grade 3 or Grade 4 adverse reaction except for Grade 3 nausea and/or vomiting controlled by antiemetic therapy or Grade 3 diarrhea responsive to antidiarrheal medication
- A maximum of 3 dose reductions are permitted to a minimum dose of 20 mg/m2 twice daily. Do not escalate LONSURF dose after it has been reduced.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Contraindications in the drug label.
Warnings
- Severe Myelosuppression
- In Study 1, LONSURF caused severe and life-threatening myelosuppression (Grade 3-4) consisting of anemia (18%), neutropenia (38%), thrombocytopenia (5%) and febrile neutropenia (3.8%). One patient (0.2%) died due to neutropenic infection. In Study 1, 9.4% of LONSURF-treated patients received granulocyte-colony stimulating factors.
- Obtain complete blood counts prior to and on Day 15 of each cycle of LONSURF and more frequently as clinically indicated. Withhold LONSURF for febrile neutropenia, Grade 4 neutropenia, or platelets less than 50,000/mm3. Upon recovery resume LONSURF at a reduced dose.
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Based on animal studies and its mechanism of action, LONSURF can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Trifluridine/tipiracil caused embryo-fetal lethality and embryo-fetal toxicity in pregnant rats when orally administered during gestation at dose levels resulting in exposures lower than those achieved at the recommended dose of 35 mg/m2 twice daily.
- Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LONSURF.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below are from Study 1, a randomized (2:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which 533 patients (median age 63 years; 61% men; 57% White, 35% Asian, 1% Black) with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer received LONSURF as a single agent at a dose of 35 mg/m2/dose administered twice daily on Days 1 through 5 and Days 8 through 12 of each 28-day cycle. The mean duration of LONSURF therapy was 12.7 weeks.
The most common adverse drug reactions or laboratory abnormalities (all Grades and greater than or equal to 10% in incidence) in patients treated with LONSURF at a rate that exceeds the rate in patients receiving placebo were anemia, neutropenia, asthenia/fatigue, nausea, thrombocytopenia, decreased appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and pyrexia.
In Study 1, 3.6% of patients discontinued LONSURF for an adverse event and 13.7% of patients required a dose reduction. The most common adverse reactions leading to dose reduction were neutropenia, anemia, febrile neutropenia, fatigue, and diarrhea.

In Study 1, infections occurred more frequently in LONSURF-treated patients (27%) compared to those receiving placebo (15%). The most commonly reported infections which occurred more frequently in LONSURF-treated patients were nasopharyngitis (4% versus 2%), and urinary tract infections (4% versus 2%).
In Study 1, pulmonary emboli occurred more frequently in LONSURF-treated patients (2%) compared to no patients on placebo.
Additional Clinical Experience:
Interstitial lung disease was reported in fifteen (0.2%) patients, three of which were fatal, among approximately 7,000 patients exposed to LONSURF in clinical studies and clinical practice settings in Asia.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Trifluridine and tipiracil in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Trifluridine and tipiracil in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Trifluridine and tipiracil during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trifluridine and tipiracil with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trifluridine and tipiracil with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Trifluridine and tipiracil in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Trifluridine and tipiracil and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Trifluridine and tipiracil |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Trifluridine and tipiracil |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Trifluridine and tipiracil interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Trifluridine and tipiracil Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.