Mastoiditis other diagnostic studies: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Other mastoiditis imaging findings include [[Otoscopy|otoscopic]] images of the [[tympanic membrane]] displaying middle ear effusion and infection. Also [[Tympanometry|tympanograms]] <nowiki/>may be used for measuring pressure from fluid buildup in the [[middle ear]]. | Other mastoiditis imaging findings include [[Otoscopy|otoscopic]] images of the [[tympanic membrane]] displaying middle ear effusion and infection. Also, [[Tympanometry|tympanograms]] <nowiki/>may be used for measuring pressure from fluid buildup in the [[middle ear]]. | ||
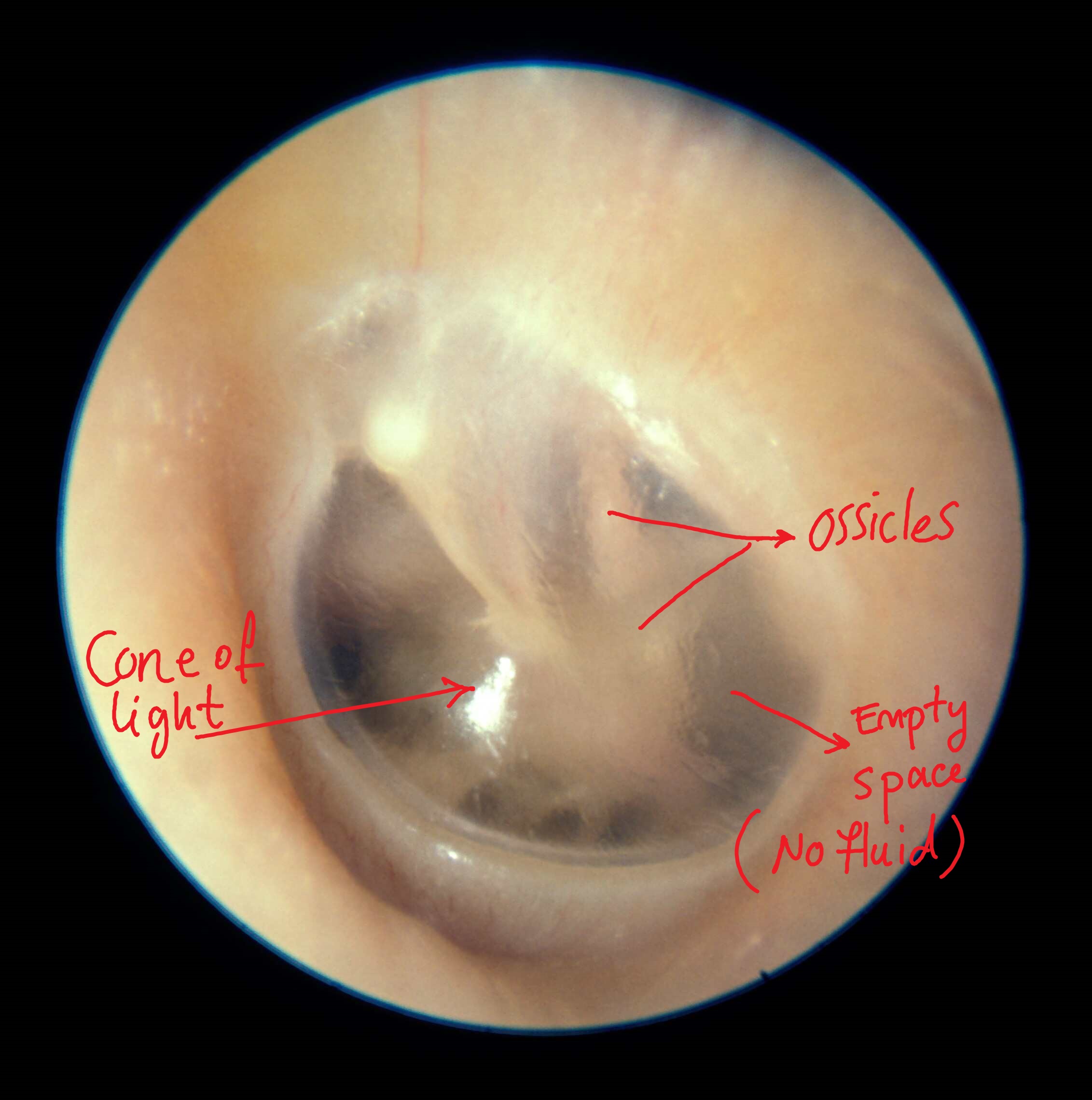
== Key Findings in Otoscopy in mastoiditis == | == Key Findings in Otoscopy in mastoiditis == | ||
[[Otoscopy|Otoscopic]] examination of the ears may reveal the following signs indicative of mastoiditis:<ref name="pmid25213276">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rettig E, Tunkel DE |title=Contemporary concepts in management of acute otitis media in children |journal=Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. |volume=47 |issue=5 |pages=651–72 |year=2014 |pmid=25213276 |pmc=4393005 |doi=10.1016/j.otc.2014.06.006 |url=}}</ref> | [[Otoscopy|Otoscopic]] examination of the ears may reveal the following signs indicative of mastoiditis:<ref name="pmid25213276">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rettig E, Tunkel DE |title=Contemporary concepts in management of acute otitis media in children |journal=Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. |volume=47 |issue=5 |pages=651–72 |year=2014 |pmid=25213276 |pmc=4393005 |doi=10.1016/j.otc.2014.06.006 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*[[Erythema]] of the [[middle ear]] | *[[Erythema]] of the [[middle ear]] | ||
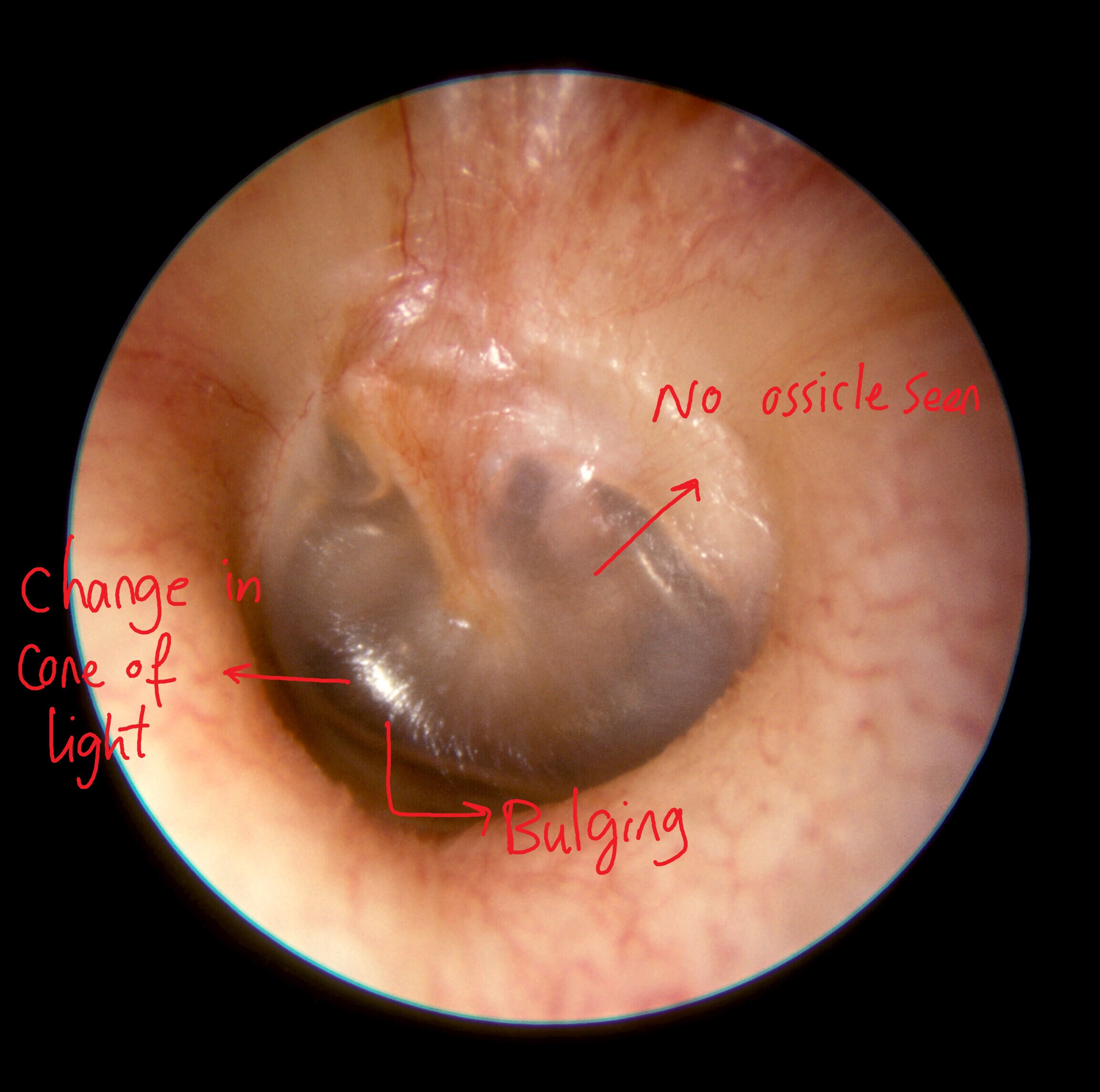
*Presence of effusion | *Presence of effusion<ref name="pmid23346249">{{cite journal |vauthors=Parlea E, Georgescu M, Calarasu R |title=Tympanometry as a predictor factor in the evolution of otitis media with effusion |journal=J Med Life |volume=5 |issue=4 |pages=452–4 |year=2012 |pmid=23346249 |pmc=3539835 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Bulging of the [[tympanic membrane]] in [[otitis media]] with effusion | *Bulging of the [[tympanic membrane]] in [[otitis media]] with effusion | ||
*Cloudy appearance of the [[tympanic membrane]] | *Cloudy appearance of the [[tympanic membrane]] | ||
*Immobility of the [[tympanic membrane]] | *Immobility of the [[tympanic membrane]] | ||
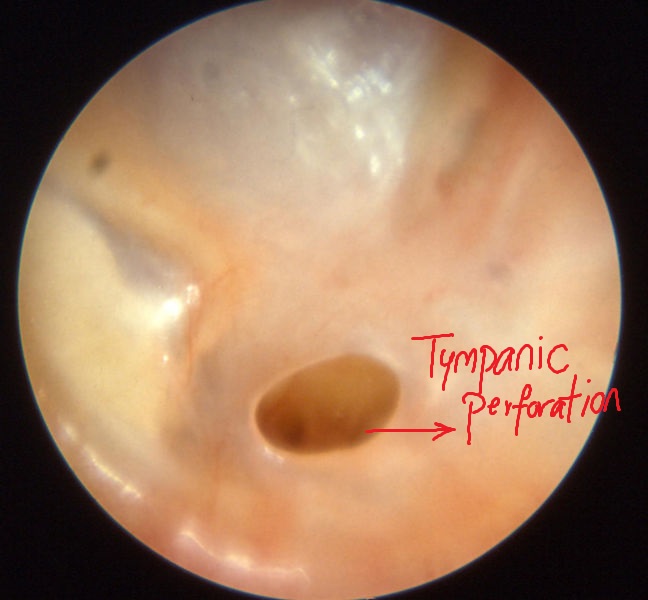
*[[Tympanic membrane]] perforation | *[[Tympanic membrane]] perforation | ||
==Examples of Otoscopy in Mastoiditis== | ==Examples of Otoscopy in Mastoiditis== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Key Findings in Tympanometry in mastoiditis== | |||
Tympanometry may reveal hearing loss due to effusion, as measured by abnormally large reflection of sound due to elevated pressure from fluid buildup.[1] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | |||
{{WS}} | |||
[[Category:Emergency mdicine]] | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | [[Category:Disease]] | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Infectious disease]] | [[Category:Infectious disease]] | ||
[[Category:Otolaryngology]] | [[Category:Otolaryngology]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Surgery]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:39, 29 July 2020
|
Mastoiditis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mehrian Jafarizade, M.D [2]
Overview
Other mastoiditis imaging findings include otoscopic images of the tympanic membrane displaying middle ear effusion and infection. Also, tympanograms may be used for measuring pressure from fluid buildup in the middle ear.
Key Findings in Otoscopy in mastoiditis
Otoscopic examination of the ears may reveal the following signs indicative of mastoiditis:[1]
- Erythema of the middle ear
- Presence of effusion[2]
- Bulging of the tympanic membrane in otitis media with effusion
- Cloudy appearance of the tympanic membrane
- Immobility of the tympanic membrane
- Tympanic membrane perforation
Examples of Otoscopy in Mastoiditis
-
Normal tympanic membrane
-
Chronic otitis media
-
Middle ear effusion
Key Findings in Tympanometry in mastoiditis
Tympanometry may reveal hearing loss due to effusion, as measured by abnormally large reflection of sound due to elevated pressure from fluid buildup.[1]
References
- ↑ Rettig E, Tunkel DE (2014). "Contemporary concepts in management of acute otitis media in children". Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 47 (5): 651–72. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2014.06.006. PMC 4393005. PMID 25213276.
- ↑ Parlea E, Georgescu M, Calarasu R (2012). "Tympanometry as a predictor factor in the evolution of otitis media with effusion". J Med Life. 5 (4): 452–4. PMC 3539835. PMID 23346249.