File:Alphavirus04.jpeg
Alphavirus04.jpeg (700 × 475 pixels, file size: 56 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Magnified 1500X, this scanning electron micrograph (SEM) revealed some of the minute exoskeletal details found at the proboscis tip of an unidentified mosquito found deceased in the suburbs of Decatur, Georgia. The proboscis is the organ used by this, as well as other like insects, to feed upon the blood of a warm-blooded host, including human beings. What you see here, is the sheath that encases a pair of needle-sharp "stylets", which together are known as the "fascicle". The larger of the two stylets, known as the "labrum", when viewed in cross-section, takes on the shape of a "V", and acts as a gutter, directing the ingested host blood towards the insect's mouth. The “hair-like” structures are known as "setae", and are really extensions of the insect's exoskeletal, chitinous covering. These setae act as sensory organs, transmitting impulses indicating changes in the organism's environment.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:55, 3 December 2014 | 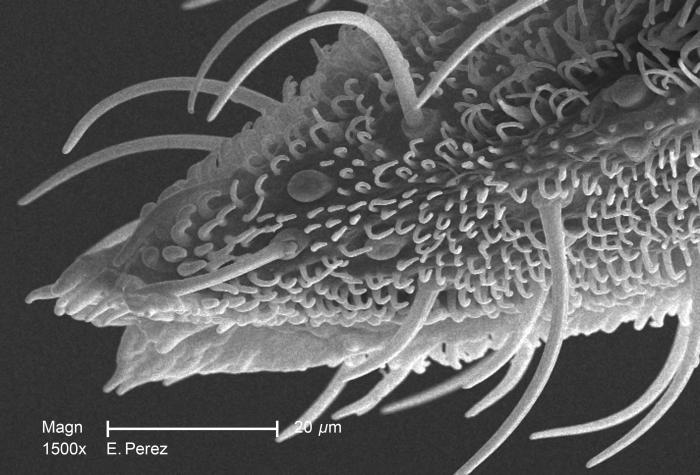 | 700 × 475 (56 KB) | Jesus Hernandez (talk | contribs) | Magnified 1500X, this scanning electron micrograph (SEM) revealed some of the minute exoskeletal details found at the proboscis tip of an unidentified mosquito found deceased in the suburbs of Decatur, Georgia. The proboscis is the organ used by this, ... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: