Bone island
|
WikiDoc Resources for Bone island |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Bone island Most cited articles on Bone island |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Bone island |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Bone island at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Bone island at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Bone island
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Bone island Discussion groups on Bone island Patient Handouts on Bone island Directions to Hospitals Treating Bone island Risk calculators and risk factors for Bone island
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Bone island |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: Enostosis
Overview
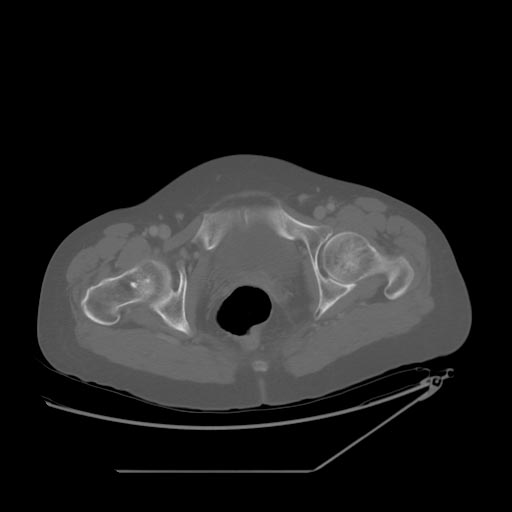
- A bone island is a focus of compact bone located in cancellous bone.
- Benign entity that is usually found incidentally on imaging studies
- Histologically, bone islands are intramedullary foci of normal compact bone with haversian canals and "thorny" radiations that merge with the trabeculae of surrounding normal cancellous bone.
- Most commonly identified in the pelvis, long bones, ribs, and spine.
Diagnosis
X-ray
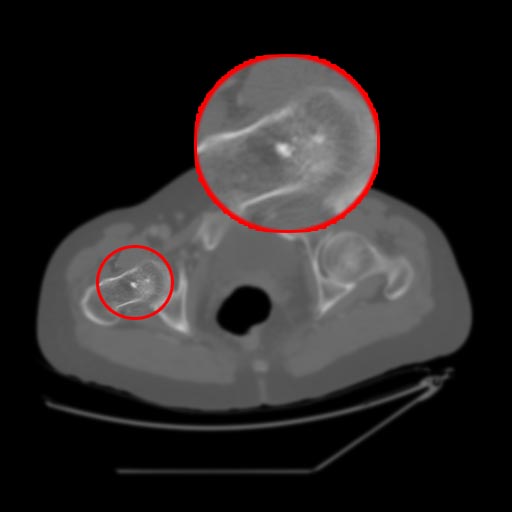
- Round or ovoid intramedullary sclerotic foci.
- Long axis of a bone island typically parallels the long axis of the involved bone. Bone islands appear homogeneously sclerotic with “thorny” radiating bone spicules that extend from the center of the lesion and blend with the trabeculae.
CT
- Same as above for plain films
MRI
- Dark on all pulse sequences